Author: everythingcryptoitclouds.com
Published: July 23, 2025
Figure 1: Data as a Service enables organizations to unlock the power of their data assets through cloud-based, on-demand access and analytics capabilities.
In today’s data-driven business landscape, organizations are drowning in information while simultaneously thirsting for actionable insights. The paradox of having access to vast amounts of data yet struggling to extract meaningful value from it has become one of the most pressing challenges facing modern enterprises. Enter Data as a Service (DaaS) – a transformative approach that promises to revolutionize how businesses access, manage, and leverage their data assets.
Data as a Service represents a fundamental shift from traditional data management paradigms, offering a cloud-native business model that provides on-demand access to high-quality, processed data through application programming interfaces (APIs) and automated delivery mechanisms [1]. Unlike conventional data management approaches that require extensive internal infrastructure, specialized expertise, and significant capital investments, DaaS platforms host data in scalable cloud environments while handling all aspects of storage, processing, governance, and security [2].
The emergence of DaaS is not merely a technological evolution; it represents a strategic response to the growing complexity of modern data ecosystems. Organizations today generate data at unprecedented rates, with estimates suggesting that the global datasphere will grow from 33 zettabytes in 2018 to 175 zettabytes by 2025 [3]. This exponential growth, coupled with the increasing sophistication of analytical requirements and the need for real-time decision-making capabilities, has created a perfect storm that traditional data management approaches simply cannot address effectively.
What makes DaaS particularly compelling is its ability to democratize data access across organizations while simultaneously addressing the technical complexities that have historically hindered data-driven initiatives. By abstracting away the underlying infrastructure and technical intricacies, DaaS enables business users to focus on extracting insights and driving value rather than grappling with data engineering challenges. This democratization effect is transforming how organizations approach data strategy, moving from centralized, IT-driven models to distributed, business-user-empowered frameworks.
The market validation for DaaS is undeniable. According to recent market research, the global Data as a Service market was valued at USD 14.36 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.1% from 2024 to 2030, potentially reaching USD 76.80 billion by the end of the decade [4]. This remarkable growth trajectory reflects not only the increasing recognition of data as a strategic asset but also the growing sophistication of cloud-based data delivery mechanisms and the maturation of supporting technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and edge computing.
However, understanding DaaS requires more than simply recognizing its market potential or technical capabilities. It demands a comprehensive examination of how this service model addresses fundamental business challenges, transforms organizational capabilities, and creates new opportunities for innovation and competitive advantage. This exploration must encompass not only the technical architecture and implementation considerations but also the strategic implications, use case applications, and future trajectory of this rapidly evolving field.
Understanding Data as a Service: Definition and Core Concepts
Data as a Service (DaaS) represents a sophisticated data management strategy that aims to leverage data as a business asset for greater organizational agility and competitive advantage [5]. At its core, DaaS is part of the broader “as a service” ecosystem that has become increasingly prevalent since the expansion of internet infrastructure in the 1990s, following the pioneering introduction of Software as a Service (SaaS) models [6].
The fundamental premise of DaaS lies in its ability to provide a unified approach to managing the massive volumes of data that organizations generate daily while delivering valuable information across the business for data-driven decision making [7]. This approach focuses specifically on provisioning data from diverse sources on demand through APIs, designed to simplify access to data while delivering curated datasets or streams of information that can be consumed in various formats, often unified through advanced data virtualization technologies [8].
Modern DaaS implementations have evolved far beyond simple data hosting services to become intelligent data ecosystems that incorporate automated quality monitoring, real-time processing capabilities, and embedded artificial intelligence for predictive analytics [9]. These platforms leverage advanced architectural patterns including data meshes, fabric technologies, and privacy-preserving computation methods to deliver data that meets enterprise governance requirements while enabling rapid innovation [10].
The architectural foundation of DaaS typically encompasses a comprehensive range of data management technologies, including data virtualization, data services, self-service analytics, and data cataloging capabilities [11]. This integrated approach enables organizations to create a unified view of their data landscape while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to changing business requirements and technological advances.
What distinguishes DaaS from traditional data management approaches is its cloud-native architecture and service-oriented delivery model. Rather than requiring organizations to invest in and maintain complex data infrastructure, DaaS providers host data in scalable cloud environments while handling all aspects of storage, processing, governance, and security [12]. This fundamental shift enables organizations to focus their resources on data analysis and business value creation rather than infrastructure management and technical maintenance.
The service delivery model of DaaS is characterized by its emphasis on accessibility and usability. Data is made available through standardized APIs that enable seamless integration with existing business applications and analytical tools [13]. This API-first approach ensures that data can be consumed by various systems and applications without requiring complex integration projects or specialized technical expertise.
Furthermore, DaaS platforms typically provide sophisticated data transformation and enrichment capabilities that enhance the value of raw data assets. These capabilities include data cleansing, normalization, enrichment with external data sources, and the application of advanced analytical models to generate insights and predictions [14]. By providing these value-added services, DaaS platforms enable organizations to derive maximum value from their data investments while reducing the time and resources required to achieve actionable insights.
The governance and security aspects of DaaS are particularly critical given the sensitive nature of organizational data assets. Modern DaaS platforms implement comprehensive security frameworks that include encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access controls, audit logging, and compliance with regulatory requirements such as GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations [15]. These security measures are designed to ensure that data remains protected throughout its lifecycle while enabling authorized users to access the information they need to perform their roles effectively.
The scalability characteristics of DaaS platforms represent another key differentiator from traditional data management approaches. Cloud-native architectures enable DaaS platforms to automatically scale resources based on demand, ensuring consistent performance even during peak usage periods [16]. This elasticity is particularly important for organizations with variable data processing requirements or those experiencing rapid growth in data volumes.
Figure 2: A comprehensive view of Data as a Service architecture showing the integration of various data sources, processing layers, and delivery mechanisms that enable seamless data access and analytics.
The Challenges DaaS Addresses: Beyond Legacy System Limitations
The emergence and rapid adoption of Data as a Service can be understood most clearly through the lens of the fundamental challenges that traditional data management approaches have failed to address effectively. These challenges have become increasingly acute as organizations grapple with exponentially growing data volumes, increasingly sophisticated analytical requirements, and the need for real-time decision-making capabilities in competitive business environments.
The Agility Crisis in Legacy Systems
Legacy data systems are fundamentally burdened by outdated technologies and complex codebases that have accumulated technical debt over years or decades of incremental development [17]. These systems are notoriously difficult to maintain, update, and extend, creating significant barriers to organizational agility and innovation. The limitations are particularly pronounced when organizations attempt to implement new analytical capabilities or integrate emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
The architectural assumptions underlying many legacy systems reflect the technological constraints and business requirements of previous decades. For example, legacy systems are often built on the assumption that data should be stored in relational databases with rigid schemas, which severely limits the flexibility of the data model and makes schema migrations a complex and risky undertaking [18]. This rigidity becomes particularly problematic as organizations seek to incorporate new data types, such as unstructured text, images, video, and IoT sensor data, that do not fit neatly into traditional relational structures.
Moreover, legacy systems typically require specialized technical expertise to operate and maintain, creating dependencies on scarce human resources and limiting the ability of business users to directly access and analyze data [19]. This technical complexity often results in lengthy development cycles for new analytical capabilities, preventing organizations from responding quickly to changing market conditions or emerging business opportunities.
Data Silos and Organizational Fragmentation
One of the most pervasive challenges in traditional data management is the creation of data silos – isolated repositories of information that are disconnected from other organizational data sources [20]. These silos emerge naturally as different departments and business units develop their own data management solutions to address specific operational requirements, but they create significant barriers to comprehensive analysis and organizational learning.
Data silos limit the ability to share information across teams and applications, fundamentally constraining the development of holistic business insights [21]. When customer data is maintained separately from product data, and both are isolated from financial information, organizations lose the ability to understand the complex relationships and dependencies that drive business performance. This fragmentation slows down analytical processes and makes it difficult to extract complete insights that could inform strategic decision-making.
The technical challenges associated with data silos are compounded by organizational and political factors. Different departments may have conflicting priorities regarding data access, quality standards, and governance policies, making it difficult to establish unified data management practices [22]. These conflicts can result in duplicated efforts, inconsistent data definitions, and reduced confidence in analytical results.
Accessibility and Real-Time Requirements
Modern business operations increasingly require data to be available in real-time, 24 hours a day, seven days a week, to support continuous operations and enable rapid response to changing conditions [23]. However, many existing data systems were not designed to meet these demanding availability and performance requirements. Legacy systems are often deployed on self-hosted servers in single physical locations, creating single points of failure that can disrupt business operations [24].
The self-hosted model also creates significant accessibility challenges, as data becomes inaccessible from locations outside the organization’s physical infrastructure [25]. This limitation has become particularly problematic as organizations adopt remote work models and seek to enable data-driven decision-making across distributed teams and geographical locations.
Furthermore, traditional batch processing approaches that were adequate for historical reporting requirements are insufficient for modern analytical use cases that require real-time insights [26]. Organizations need the ability to analyze streaming data, detect anomalies as they occur, and trigger automated responses to changing conditions, capabilities that are difficult to implement with legacy architectures.
Scaling Limitations and Performance Constraints
Traditional relational databases are designed to scale vertically by adding more processing power to existing machines, rather than scaling horizontally by distributing processing across multiple machines [27]. This architectural limitation becomes a significant constraint as data volumes grow and analytical complexity increases. Vertical scaling is not only expensive but also has practical limits that can be reached relatively quickly in data-intensive applications.
Legacy systems are often designed as single-tenant applications deployed in single physical locations, making it difficult to achieve the horizontal scaling required for modern data workloads [28]. This limitation is particularly problematic for organizations experiencing rapid growth in data volumes or those seeking to implement advanced analytical capabilities that require significant computational resources.
The performance constraints of legacy systems are further exacerbated by their inability to take advantage of modern cloud computing capabilities, including elastic scaling, distributed processing, and specialized analytical hardware [29]. Organizations remain constrained by their existing infrastructure investments and cannot easily adapt to changing performance requirements or take advantage of technological advances.
Data Variety and Schema Rigidity
The explosion of new data types generated by web applications, mobile devices, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices has created challenges that legacy systems are fundamentally ill-equipped to handle [30]. These new data sources produce information in volumes and varieties that exceed the capabilities of traditional data management approaches, which are often limited to structured data that conforms to predefined schemas.
Legacy systems typically lack support for unstructured data such as text documents, images, video files, and sensor readings, forcing organizations to either ignore valuable information sources or invest in separate systems to handle different data types [31]. This fragmentation increases complexity and costs while reducing the organization’s ability to develop comprehensive analytical insights that incorporate all available information sources.
The schema rigidity of traditional systems also makes it difficult to adapt to changing business requirements or incorporate new data sources [32]. When business processes evolve or new analytical requirements emerge, organizations often face lengthy and expensive schema migration projects that can disrupt operations and delay the implementation of new capabilities.
The Transformative Benefits of Data as a Service
The adoption of Data as a Service delivers a comprehensive range of benefits that address the fundamental limitations of traditional data management approaches while creating new opportunities for organizational growth and competitive advantage. These benefits extend beyond simple technical improvements to encompass strategic, operational, and financial advantages that can transform how organizations create and capture value from their data assets.
Data Monetization and Strategic Value Creation
One of the most significant benefits of DaaS is its ability to unlock the monetization potential of organizational data assets [33]. Having sufficient data is no longer a primary challenge for most organizations; the critical issue has become organizing and operationalizing that data to extract maximum value. While many executives have invested heavily in data monetization initiatives, very few have successfully leveraged the full potential of their data assets, largely due to the technical and organizational barriers associated with traditional data management approaches.
DaaS addresses this challenge by increasing data accessibility and enabling organizations to develop new revenue streams from their information assets [34]. By providing standardized APIs and self-service access capabilities, DaaS platforms enable organizations to package and distribute their data assets to internal and external consumers, creating new business models and revenue opportunities. This capability is particularly valuable for organizations with unique or proprietary data sets that could provide value to partners, customers, or third-party developers.
The strategic value of data monetization extends beyond direct revenue generation to include improved customer relationships, enhanced partner ecosystems, and strengthened competitive positioning [35]. Organizations that can effectively leverage their data assets through DaaS platforms often discover new insights about their customers, markets, and operations that inform strategic decision-making and drive innovation initiatives.
Cost Reduction and Operational Efficiency
DaaS delivers significant cost reductions by eliminating the need for organizations to invest in and maintain complex data infrastructure [36]. Traditional data management approaches require substantial capital expenditures for hardware, software licenses, and specialized personnel, along with ongoing operational expenses for maintenance, upgrades, and support. DaaS platforms shift these costs to a service provider while converting fixed infrastructure costs to variable operational expenses that scale with actual usage.
The operational efficiency benefits of DaaS extend beyond simple cost reduction to include improved resource allocation and reduced time-to-value for data initiatives [37]. By capitalizing on all of an organization’s data sources and delivering insights to different business areas, DaaS enables more informed decision-making that reduces waste and improves operational performance. Organizations report significant reductions in time and money spent on incorrect decisions when they transition from intuition-based to data-driven decision-making processes.
Furthermore, DaaS platforms can help organizations develop personalized customer experiences by leveraging predictive analytics to understand consumer behaviors and patterns [38]. This capability enables organizations to better serve customers, increase satisfaction levels, and build stronger customer loyalty, ultimately driving revenue growth and market share expansion.
Accelerated Innovation and Competitive Advantage
DaaS serves as a catalyst for innovation by providing organizations with the data foundation necessary to support advanced analytical initiatives and emerging technologies [39]. When trustworthy, high-quality data is readily available to different departments and teams, ideas based on that data have a significantly higher probability of gaining organizational support and succeeding when implemented. This accessibility reduces the barriers to innovation and enables organizations to experiment with new approaches and technologies more rapidly and cost-effectively.
The innovation benefits of DaaS are particularly pronounced in the context of artificial intelligence and machine learning initiatives [40]. These technologies require large volumes of high-quality, well-structured data to train models and generate accurate predictions. DaaS platforms provide the data infrastructure and preprocessing capabilities necessary to support AI/ML initiatives while reducing the time and resources required to prepare data for analytical applications.
Organizations that effectively leverage DaaS often discover that data-informed strategies enable more innovation with reduced risk [41]. When decisions are based on comprehensive data analysis rather than intuition or limited information, organizations can pursue more ambitious initiatives with greater confidence in their potential success. This capability is particularly valuable in competitive markets where the ability to innovate rapidly can determine market leadership and long-term success.
Enhanced Decision-Making Agility
Data as a Service represents a transformative opportunity for organizations to treat data as a strategic business asset for more effective decision-making and improved data management practices [42]. DaaS platforms can combine both internal and external data sources, including customer data, partner information, and open data sources, to provide comprehensive views of business operations and market conditions.
The agility benefits of DaaS are particularly evident in its ability to quickly deliver data for purpose-built analytics through end-to-end APIs serving specific business use cases [43]. This capability enables organizations to respond rapidly to changing market conditions, customer requirements, or competitive pressures by quickly accessing and analyzing relevant data to inform strategic responses.
DaaS platforms also support self-service data access, simplifying business user interactions with data through intuitive, self-service directories and interfaces [44]. This democratization of data access reduces the time spent searching for information and increases the time available for analysis and action, enabling more agile decision-making processes throughout the organization.
Cultural Transformation and Data Democratization
Breaking down data silos and providing teams with access to the information they need represents one of the most significant organizational challenges facing modern businesses [45]. DaaS addresses this challenge by enabling organizations to deliver integrated data from growing lists of data sources, fostering data-driven cultures and democratizing the use of data in everyday business processes.
The cultural transformation enabled by DaaS extends beyond simple data access to include the development of reusable data assets that promote both inter-enterprise and intra-enterprise sharing [46]. These reusable datasets establish central understanding of business operations and performance while enabling different teams and departments to build upon each other’s analytical work rather than duplicating efforts.
By opening access to critical data resources, DaaS helps organizations infuse data into their business practices at all levels, from operational decision-making to strategic planning [47]. This comprehensive integration of data into business processes creates competitive advantages that are difficult for competitors to replicate and provides sustainable foundations for long-term success.
Risk Mitigation and Governance Enhancement
DaaS platforms help organizations remove personal biases from decision-making processes that often put companies at risk [48]. Organizations that rely primarily on intuition and experience for decision-making face significant risks in rapidly changing business environments. DaaS empowers organizations with data-driven insights that enable more accurate assessments of risks and opportunities, leading to better strategic decisions and improved business outcomes.
The risk mitigation benefits of DaaS extend to data governance and security considerations [49]. Modern DaaS platforms leverage data virtualization and other advanced technologies to access, combine, transform, and deliver data through reusable data services while optimizing query performance and ensuring data security and governance compliance. This approach helps organizations avoid risks associated with conflicting or incomplete data views, poor data quality, and regulatory non-compliance.
Furthermore, DaaS platforms typically implement comprehensive audit trails and access controls that provide organizations with detailed visibility into how their data is being used and by whom [50]. This transparency is essential for regulatory compliance and risk management, particularly in industries with strict data governance requirements such as healthcare, financial services, and government sectors.
Primary Use Cases and Applications of Data as a Service
The practical applications of Data as a Service span across industries and functional areas, demonstrating the versatility and transformative potential of this approach to data management. Understanding these use cases provides insight into how organizations can leverage DaaS to address specific business challenges and create competitive advantages in their respective markets.
Creating Unified Enterprise Data Views
One of the most impactful applications of DaaS involves enabling organizations to construct comprehensive business intelligence by seamlessly integrating internal operational data with external market intelligence [51]. This unified approach eliminates the data silos that traditionally prevent cross-functional analysis, enabling teams to understand customer journeys, operational efficiency, and market positioning through a single analytical framework.
Modern DaaS implementations extend beyond simple data consolidation to provide contextualized intelligence that adapts to specific business roles and responsibilities [52]. Sales teams receive customer insights enhanced with market trends and competitive intelligence, enabling them to develop more effective sales strategies and improve customer relationships. Operations teams access supply chain data enriched with external factors including weather patterns, economic indicators, and regulatory changes that impact business performance, allowing them to optimize operations and mitigate risks proactively.
The unified data view capability is particularly valuable for organizations operating in complex, multi-channel business environments where customer interactions span multiple touchpoints and systems [53]. By integrating data from customer relationship management systems, e-commerce platforms, social media channels, and customer service interactions, organizations can develop comprehensive customer profiles that inform personalized marketing strategies, product development initiatives, and customer service improvements.
Financial services organizations, for example, leverage unified data views to combine transaction data, market information, regulatory updates, and customer behavior patterns to develop comprehensive risk assessments and investment strategies [54]. This integrated approach enables more accurate risk modeling, improved compliance monitoring, and enhanced customer service delivery across all business channels.
Powering Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning
DaaS platforms serve as the foundational infrastructure for sophisticated analytical applications that require clean, consistent, and current data inputs [55]. These platforms handle the complex preprocessing requirements including feature engineering, data validation, and schema management that enable machine learning models to operate reliably in production environments without manual intervention.
The preprocessing capabilities of DaaS platforms are particularly critical for machine learning applications, which require data to be formatted, cleaned, and structured in specific ways to achieve optimal model performance [56]. Traditional approaches to data preparation for machine learning can consume 80% or more of a data scientist’s time, significantly reducing the resources available for model development and optimization. DaaS platforms automate these preprocessing tasks, enabling data science teams to focus on model development and business value creation.
Advanced analytics use cases enabled by DaaS include predictive maintenance systems that combine equipment sensor data with external factors such as weather conditions and usage patterns to predict equipment failures before they occur [57]. These systems enable organizations to optimize maintenance schedules, reduce unplanned downtime, and extend equipment lifecycles, resulting in significant cost savings and operational improvements.
Fraud detection represents another critical application area where DaaS platforms provide substantial value [58]. These systems correlate transaction patterns with real-time risk intelligence from multiple sources, including credit bureaus, law enforcement databases, and behavioral analytics platforms, to identify potentially fraudulent activities with high accuracy and minimal false positives. The real-time nature of DaaS platforms enables immediate response to detected threats, minimizing financial losses and protecting customer assets.
Dynamic pricing models represent a sophisticated application of DaaS that integrates inventory levels with market demand signals, competitor pricing information, and customer behavior patterns to optimize pricing strategies in real-time [59]. Retail organizations use these systems to maximize revenue and profit margins while maintaining competitive positioning and customer satisfaction.
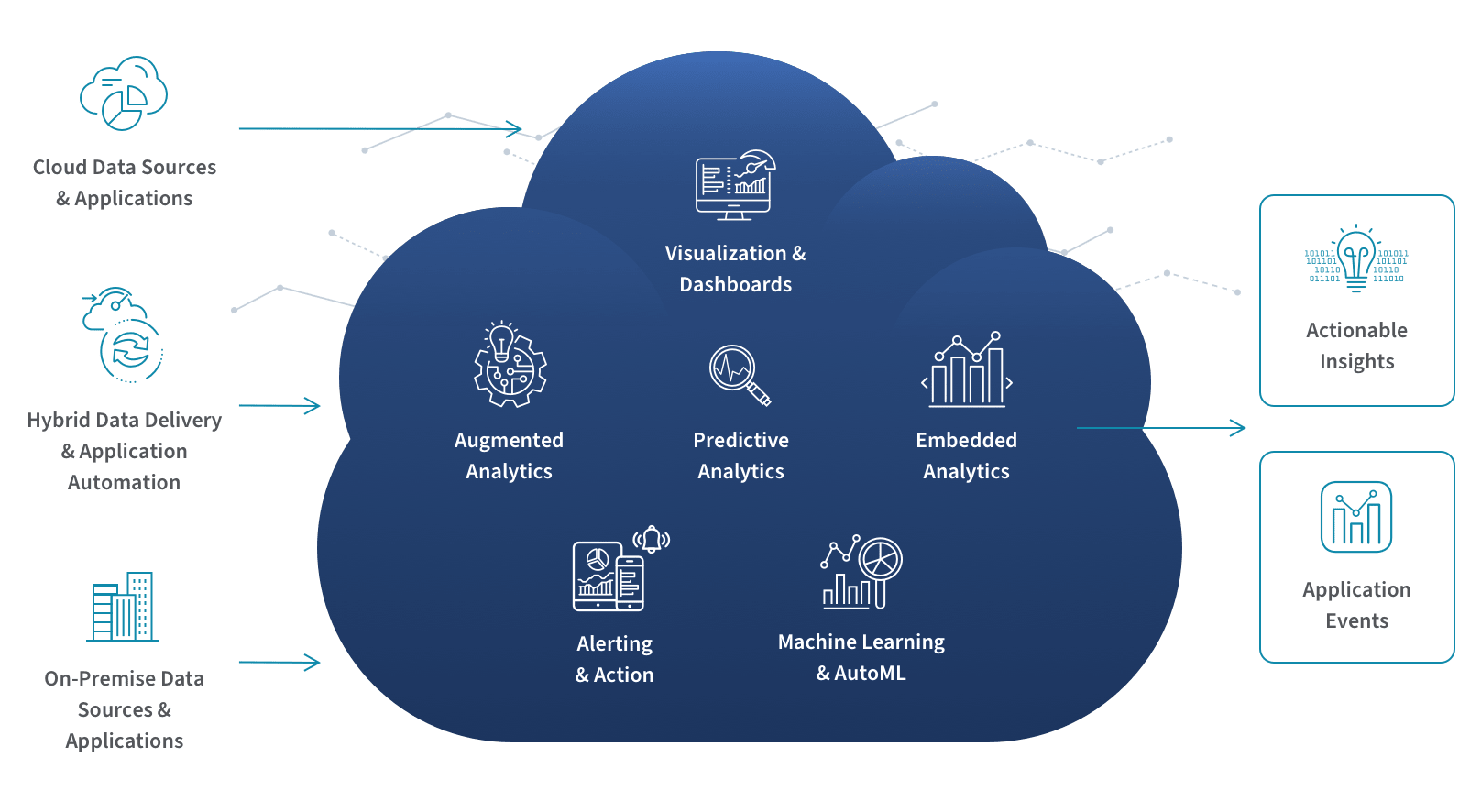
Figure 3: The cloud analytics process showing how DaaS platforms enable organizations to ingest, process, store, and analyze data to generate actionable business insights.
Enabling Real-Time Operational Intelligence
Contemporary DaaS implementations provide the real-time data streams that power operational applications including supply chain optimization, customer service personalization, and dynamic resource allocation [60]. These applications require data latencies measured in seconds rather than hours, with automatic scaling capabilities that handle usage spikes without performance degradation.
Real-time operational intelligence applications leverage DaaS to combine multiple data streams simultaneously, enabling immediate responses to changing business conditions [61]. Inventory management systems automatically adjust procurement decisions based on sales velocity, supplier availability, seasonal trends, and market conditions, ensuring optimal inventory levels while minimizing carrying costs and stockout risks.
Customer service platforms represent another critical application area where real-time operational intelligence creates significant value [62]. These systems provide customer service representatives with comprehensive customer context during interactions, including purchase history, previous service interactions, current account status, and relevant product information. This comprehensive view enables more effective problem resolution, improved customer satisfaction, and increased opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
Marketing automation systems leverage real-time operational intelligence to personalize content and offers based on current customer behavior, preferences, and engagement patterns [63]. These systems can adjust marketing messages, product recommendations, and promotional offers in real-time based on customer interactions, significantly improving conversion rates and customer engagement levels.
Industry-Specific Applications
The healthcare industry has emerged as a significant adopter of DaaS platforms, leveraging these systems to integrate patient data from multiple sources including electronic health records, medical devices, laboratory systems, and imaging platforms [64]. This integrated approach enables healthcare providers to develop comprehensive patient profiles that inform treatment decisions, identify potential health risks, and optimize care delivery processes.
Pharmaceutical companies use DaaS platforms to integrate clinical trial data, regulatory information, market research, and competitive intelligence to accelerate drug development processes and optimize market entry strategies [65]. These applications enable more efficient clinical trial design, improved patient recruitment, and enhanced regulatory compliance monitoring.
The financial services industry leverages DaaS for applications including risk management, regulatory compliance, algorithmic trading, and customer analytics [66]. Investment firms use DaaS platforms to integrate market data, economic indicators, company financial information, and alternative data sources to develop sophisticated trading strategies and risk management frameworks.
Manufacturing organizations implement DaaS platforms to integrate production data, supply chain information, quality metrics, and maintenance records to optimize manufacturing processes and improve product quality [67]. These applications enable predictive maintenance, quality control optimization, and supply chain risk management that reduce costs and improve operational efficiency.
Departmental Applications Across Organizations
Sales and marketing departments leverage DaaS platforms to integrate customer data, market research, competitive intelligence, and campaign performance metrics to develop more effective marketing strategies and sales processes [68]. These applications enable improved lead scoring, customer segmentation, campaign optimization, and sales forecasting that drive revenue growth and market share expansion.
Supply chain and inventory management teams use DaaS platforms to integrate supplier data, logistics information, demand forecasts, and market conditions to optimize procurement decisions and inventory levels [69]. These applications enable improved supplier relationship management, reduced inventory carrying costs, and enhanced customer service levels through improved product availability.
Human resources departments implement DaaS platforms to integrate employee data, performance metrics, compensation information, and market benchmarks to optimize talent management processes [70]. These applications enable improved recruiting effectiveness, enhanced employee retention, and more effective performance management that drives organizational success.
Research and development teams leverage DaaS platforms to integrate market research, competitive intelligence, customer feedback, and technical data to inform product development decisions and innovation strategies [71]. These applications enable more effective product roadmap planning, reduced time-to-market for new products, and improved alignment between product features and customer requirements.
Figure 4: Modern business intelligence dashboards powered by DaaS platforms provide comprehensive, real-time insights that enable data-driven decision making across all organizational levels.
Implementation Considerations and Challenges
While Data as a Service offers transformative potential for organizations seeking to modernize their data management capabilities, successful implementation requires careful consideration of various technical, organizational, and strategic factors. Understanding these considerations and potential challenges is essential for organizations to develop realistic implementation plans and achieve their desired outcomes.
Complexity and Scope Management
The first and perhaps most significant challenge organizations face when implementing DaaS is managing the inherent complexity of dealing with data across the entire organization rather than focusing on individual departments or specific problems [72]. DaaS initiatives typically require comprehensive roadmaps that address data sources, integration requirements, governance policies, and user needs across multiple business units and functional areas.
This organizational scope creates unique project management challenges that differ significantly from traditional technology implementations [73]. Unlike software deployments that can be rolled out incrementally to specific user groups, DaaS implementations often require coordination across multiple departments, each with different data requirements, quality standards, and operational priorities. The complexity is particularly pronounced for large corporations that have accumulated diverse, unstructured datasets over many years of operations.
Effective scope management requires organizations to develop phased implementation approaches that balance comprehensive coverage with manageable project complexity [74]. Many successful DaaS implementations begin with specific use cases or business units that can demonstrate clear value and serve as proof-of-concept for broader organizational adoption. This approach enables organizations to build internal expertise and confidence while managing implementation risks and resource requirements.
The technical complexity of DaaS implementations is further compounded by the need to integrate with existing systems and processes while maintaining operational continuity [75]. Organizations must carefully plan data migration strategies, system integration approaches, and user training programs to ensure smooth transitions that minimize business disruption and maximize user adoption.
Organizational Change Management
DaaS implementations often require fundamental changes to organizational culture, processes, and decision-making frameworks that extend far beyond technology deployment [76]. These initiatives frequently represent part of larger endeavors to make organizations more data-driven, break down departmental silos, and democratize data access across business units.
The cultural transformation required for successful DaaS adoption often necessitates direction and support from executive leadership, particularly C-suite executives who can provide the authority and resources necessary to drive organizational change [77]. Without strong leadership commitment, DaaS initiatives may encounter resistance from departments that are comfortable with existing processes or concerned about losing control over their data assets.
Change management challenges are particularly acute in organizations with established data governance structures and processes [78]. Different departments may have developed their own data quality standards, access controls, and analytical approaches that must be harmonized with enterprise-wide DaaS platforms. This harmonization process requires careful negotiation and compromise to ensure that departmental needs are met while achieving organizational objectives.
Training and skill development represent additional organizational challenges that must be addressed for successful DaaS implementation [79]. Business users who have traditionally relied on IT departments for data access and analysis must develop new skills and comfort levels with self-service data platforms. Similarly, IT professionals must adapt to new roles focused on platform management and governance rather than direct data delivery and analysis.
Security and Governance Frameworks
Given the increasingly sophisticated nature of data security threats and regulatory requirements, security considerations represent critical success factors for DaaS implementations [80]. Organizations must ensure that appropriate data governance, security, privacy, and quality controls are applied to all DaaS components while maintaining the accessibility and usability that make these platforms valuable.
The security framework for DaaS platforms must address multiple layers of protection, including network security, application security, data encryption, access controls, and audit logging [81]. These security measures must be designed to protect data throughout its lifecycle, from initial collection and storage through processing, analysis, and eventual archival or deletion.
Regulatory compliance represents an additional complexity that varies significantly across industries and geographical regions [82]. Organizations operating in healthcare, financial services, or government sectors face particularly stringent requirements for data protection, privacy, and audit trails that must be incorporated into DaaS platform design and operations.
Data governance frameworks for DaaS platforms must balance accessibility with control, enabling self-service data access while maintaining appropriate oversight and quality standards [83]. This balance requires sophisticated role-based access controls, automated data quality monitoring, and comprehensive audit capabilities that provide visibility into data usage patterns and potential security risks.
Privacy-preserving technologies such as differential privacy, federated learning, and homomorphic encryption are becoming increasingly important components of DaaS security frameworks [84]. These technologies enable organizations to extract value from sensitive data while protecting individual privacy and complying with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
Integration and Interoperability Challenges
The integration of DaaS platforms with existing organizational systems and processes represents a significant technical challenge that requires careful planning and execution [85]. Organizations typically have substantial investments in existing data infrastructure, analytical tools, and business applications that must continue to operate during and after DaaS implementation.
API design and management become critical considerations for DaaS implementations, as these interfaces serve as the primary mechanism for data access and integration [86]. Organizations must develop comprehensive API strategies that address versioning, documentation, security, performance monitoring, and lifecycle management to ensure reliable and scalable data access.
Data format standardization and transformation capabilities are essential for enabling interoperability between DaaS platforms and existing systems [87]. Organizations often maintain data in multiple formats and structures that must be harmonized to enable comprehensive analysis and reporting. This harmonization process requires sophisticated data transformation capabilities and careful attention to data quality and consistency.
The integration challenge is further complicated by the need to maintain real-time or near-real-time data synchronization between DaaS platforms and operational systems [88]. Organizations must implement robust data pipeline architectures that can handle high-volume, high-velocity data flows while maintaining data quality and consistency across all systems.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
DaaS platforms must be designed to handle varying workload patterns and usage spikes without performance degradation [89]. Organizations often experience significant variations in data access patterns based on business cycles, reporting requirements, and analytical initiatives that require elastic scaling capabilities.
Query performance optimization becomes particularly important as DaaS platforms must support diverse analytical workloads ranging from simple reporting queries to complex machine learning model training [90]. These different workload types have varying performance requirements and resource consumption patterns that must be balanced to ensure optimal platform performance.
Data caching and optimization strategies are essential for maintaining acceptable response times while managing infrastructure costs [91]. Organizations must implement intelligent caching mechanisms that balance data freshness requirements with performance optimization, particularly for frequently accessed datasets and analytical results.
The geographic distribution of users and data sources creates additional performance considerations for global organizations [92]. DaaS platforms must be designed to minimize latency and maximize availability across multiple regions while maintaining data consistency and compliance with local regulations.
Cost Management and ROI Measurement
While DaaS platforms can deliver significant cost savings compared to traditional data infrastructure, organizations must carefully manage implementation and operational costs to achieve desired return on investment [93]. The subscription-based pricing models of most DaaS platforms require organizations to accurately forecast usage patterns and optimize resource consumption to control costs.
Cost optimization strategies must address both direct platform costs and indirect costs associated with data storage, processing, and transfer [94]. Organizations must implement monitoring and optimization processes that track resource utilization and identify opportunities for cost reduction without compromising performance or functionality.
Return on investment measurement for DaaS implementations requires comprehensive metrics that capture both quantitative benefits such as cost savings and productivity improvements, and qualitative benefits such as improved decision-making and innovation capabilities [95]. Organizations must establish baseline measurements and tracking mechanisms to demonstrate the value of their DaaS investments to stakeholders and justify continued investment in platform capabilities.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The Data as a Service market is experiencing unprecedented growth driven by technological advances, changing business requirements, and the increasing recognition of data as a strategic asset. Understanding current market trends and future projections provides valuable insight into the trajectory of DaaS adoption and the opportunities available to organizations considering these platforms.
Market Growth and Economic Impact
The global Data as a Service market demonstrates remarkable growth momentum, with market size estimated at USD 14.36 billion in 2023 and projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.1% from 2024 to 2030 [96]. This growth trajectory suggests the market could reach USD 76.80 billion by the end of the decade, representing one of the fastest-growing segments in the broader cloud services market.
Alternative market projections indicate even more aggressive growth scenarios, with some analysts forecasting the DaaS market to reach USD 24.89 billion in 2025 and grow at a CAGR of 20% to reach USD 61.93 billion by 2030 [97]. These variations in market projections reflect the dynamic nature of the DaaS market and the challenges associated with precisely defining market boundaries in rapidly evolving technology sectors.
The economic impact of DaaS extends beyond direct market revenues to include significant productivity improvements and cost savings for adopting organizations [98]. Industry studies suggest that organizations implementing DaaS platforms typically achieve 20-30% reductions in data management costs while simultaneously improving data accessibility and analytical capabilities. These economic benefits are driving increased investment in DaaS platforms across industries and organizational sizes.
The market growth is particularly pronounced in specific industry verticals, with healthcare, financial services, retail, and manufacturing leading adoption rates [99]. These industries face unique data challenges related to regulatory compliance, customer experience, operational efficiency, and competitive differentiation that make DaaS platforms particularly valuable for addressing business requirements.
Technological Innovation and Integration Trends
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities into DaaS platforms represents one of the most significant technological trends shaping the market [100]. AI-powered analytics provide deeper insights and predictive capabilities that help organizations anticipate trends and make more informed decisions. These technologies enable real-time data processing and automated decision-making that enhance operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
Advanced analytics capabilities are becoming standard features of DaaS platforms, with providers continually enhancing their offerings with cutting-edge AI and ML tools [101]. These enhancements include automated data preparation, intelligent data discovery, predictive modeling, and natural language query interfaces that make advanced analytics accessible to business users without specialized technical expertise.
The growing adoption of graph databases and the need for sophisticated solutions to handle data with complex relationships are driving innovation in DaaS platform architectures [102]. Graph databases enable efficient storage and querying of complex relationships between data entities, which is particularly important in industries such as finance, healthcare, and social media where data relationships are critical to decision-making processes.
Edge computing integration represents another significant technological trend that is reshaping DaaS platform capabilities [103]. As the volume of data generated at the edge continues to grow with the proliferation of IoT devices and sensors, there is increasing demand for DaaS solutions that can process and analyze data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements while improving real-time decision-making capabilities.
Privacy and Regulatory Compliance Evolution
The increasing focus on data privacy and regulatory compliance is driving significant innovation in privacy-preserving analytics within DaaS solutions [104]. This trend encompasses techniques such as differential privacy, federated learning, and homomorphic encryption that enable data analysis while protecting sensitive information and complying with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
Privacy-preserving technologies are becoming essential components of DaaS platforms as organizations seek to balance data utilization with privacy protection and regulatory compliance [105]. These technologies enable organizations to extract value from sensitive data while maintaining customer trust and avoiding regulatory penalties that can be substantial in many jurisdictions.
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with new privacy and data protection regulations being implemented across multiple jurisdictions [106]. DaaS platforms must adapt to these changing requirements while maintaining functionality and performance, creating ongoing challenges and opportunities for platform providers and adopting organizations.
Compliance automation is emerging as a critical capability for DaaS platforms, with automated monitoring, reporting, and audit trail generation becoming standard features [107]. These capabilities reduce the administrative burden associated with regulatory compliance while providing organizations with greater confidence in their ability to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
Industry Consolidation and Market Maturation
The DaaS market is experiencing significant merger and acquisition activity as companies seek to strengthen their positions in the data services market [108]. This consolidation trend is driven by the increasing recognition of data’s strategic importance and the desire to enhance capabilities through strategic acquisitions that provide access to new technologies, customer bases, and market segments.
Platform standardization and interoperability are becoming increasingly important as the market matures and organizations seek to avoid vendor lock-in while maximizing the value of their data investments [109]. Industry standards and open-source initiatives are emerging to address these requirements and enable greater flexibility in platform selection and integration.
The competitive landscape is evolving rapidly, with traditional enterprise software vendors, cloud service providers, and specialized data companies all competing for market share [110]. This competition is driving innovation and improving platform capabilities while also creating challenges for organizations seeking to select optimal solutions for their specific requirements.
Partnership ecosystems are becoming increasingly important for DaaS platform success, with providers developing extensive networks of technology partners, system integrators, and industry specialists [111]. These partnerships enable more comprehensive solutions and faster implementation while reducing risks for adopting organizations.
Future Technology Integration
The integration of emerging technologies such as quantum computing, blockchain, and advanced artificial intelligence is expected to create new capabilities and use cases for DaaS platforms [112]. Quantum computing could enable new types of analytical capabilities that are currently computationally infeasible, while blockchain technologies could provide enhanced security and trust mechanisms for data sharing and collaboration.
Autonomous data management capabilities are emerging as a significant trend, with DaaS platforms incorporating self-healing, self-optimizing, and self-securing capabilities that reduce operational overhead and improve reliability [113]. These autonomous capabilities leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence to continuously optimize platform performance and security without human intervention.
The convergence of DaaS with other emerging technology trends such as the metaverse, augmented reality, and Internet of Things is creating new opportunities for data visualization, interaction, and analysis [114]. These convergent technologies could fundamentally change how users interact with data and extract insights from complex datasets.
Organizational Adoption Patterns
Small and medium-sized enterprises are increasingly adopting DaaS platforms as these solutions become more accessible and affordable [115]. Cloud-based delivery models and subscription pricing make advanced data management capabilities available to organizations that previously could not justify the investment in traditional data infrastructure.
The democratization of data analytics through DaaS platforms is enabling new roles and responsibilities within organizations, with business analysts, product managers, and operational staff gaining direct access to data and analytical capabilities [116]. This trend is reducing dependence on specialized IT resources while enabling more agile and responsive decision-making processes.
Cross-industry collaboration and data sharing are becoming more common as DaaS platforms provide secure mechanisms for organizations to share data and insights with partners, suppliers, and customers [117]. These collaborative capabilities are creating new business models and value creation opportunities that were previously difficult to implement with traditional data management approaches.
Conclusion: The Strategic Imperative of Data as a Service
Data as a Service represents more than a technological evolution; it embodies a fundamental transformation in how organizations conceptualize, manage, and extract value from their data assets. As we have explored throughout this comprehensive analysis, DaaS addresses critical limitations of traditional data management approaches while creating new opportunities for innovation, competitive advantage, and business value creation.
The compelling business case for DaaS adoption is evident across multiple dimensions. Organizations implementing these platforms typically achieve significant cost reductions through the elimination of complex data infrastructure investments while simultaneously improving data accessibility, quality, and analytical capabilities. The democratization of data access enabled by DaaS platforms empowers business users throughout organizations to make more informed decisions based on comprehensive, real-time information rather than intuition or limited datasets.
The market validation for DaaS is undeniable, with projected growth rates exceeding 28% annually and market values expected to reach tens of billions of dollars within the current decade. This growth reflects not only the increasing recognition of data as a strategic asset but also the maturation of supporting technologies including artificial intelligence, machine learning, cloud computing, and edge analytics that make sophisticated data services accessible to organizations of all sizes.
However, successful DaaS implementation requires more than simply selecting and deploying a platform. Organizations must carefully consider the complexity of enterprise-wide data integration, the organizational change management requirements, and the security and governance frameworks necessary to protect sensitive information while enabling productive data utilization. The most successful DaaS implementations are those that address these challenges through comprehensive planning, strong executive leadership, and phased approaches that build organizational capabilities and confidence over time.
The future trajectory of DaaS is characterized by continued technological innovation, expanding use cases, and increasing integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, edge computing, and privacy-preserving analytics. Organizations that establish strong foundations in DaaS capabilities today will be well-positioned to leverage these future innovations and maintain competitive advantages in increasingly data-driven business environments.
The strategic imperative for DaaS adoption extends beyond immediate operational benefits to encompass long-term organizational capabilities and competitive positioning. In an era where data-driven decision-making has become essential for business success, organizations that fail to modernize their data management approaches risk falling behind competitors who can more effectively leverage their information assets for strategic advantage.
As organizations evaluate their data management strategies and consider DaaS adoption, they should focus not only on immediate technical requirements but also on the broader organizational transformation that these platforms enable. The most successful DaaS implementations are those that view data as a strategic asset and leverage DaaS platforms as enablers of cultural change, innovation, and competitive differentiation rather than simply as technical solutions to data management challenges.
The journey toward effective DaaS implementation may be complex, but the potential rewards – including improved decision-making, enhanced operational efficiency, accelerated innovation, and sustainable competitive advantage – make this transformation essential for organizations seeking success in the digital economy. The question is not whether organizations should adopt DaaS capabilities, but rather how quickly and effectively they can implement these platforms to realize their transformative potential.
References
[1] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[2] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[3] IDC. “The Digitization of the World From Edge to Core.” https://www.seagate.com/files/www-content/our-story/trends/files/idc-seagate-dataage-whitepaper.pdf
[4] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[5] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[6] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[7] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[8] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[9] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[10] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[11] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[12] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[13] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[14] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[15] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[16] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[17] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[18] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[19] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[20] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[21] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[22] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[23] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[24] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[25] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[26] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[27] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[28] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[29] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[30] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[31] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[32] MongoDB. “What Is Data As A Service (DaaS)? | Full Explanation.” https://www.mongodb.com/solutions/use-cases/data-as-a-service
[33] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[34] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[35] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[36] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[37] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[38] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[39] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[40] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[41] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[42] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[43] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[44] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[45] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[46] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[47] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[48] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[49] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[50] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[51] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[52] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[53] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[54] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[55] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[56] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[57] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[58] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[59] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[60] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[61] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[62] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[63] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[64] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[65] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[66] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[67] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[68] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[69] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[70] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[71] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[72] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[73] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[74] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[75] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[76] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[77] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[78] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[79] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[80] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[81] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[82] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[83] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[84] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[85] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[86] Monda. “Data-as-a-Service Examples: Best DaaS Business Examples.” https://www.monda.ai/blog/data-as-a-service-examples
[87] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[88] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[89] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[90] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[91] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[92] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[93] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[94] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[95] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[96] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[97] Mordor Intelligence. “Data as a Service Market – Size, Share & Industry Trends.” https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/data-as-a-service-market
[98] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[99] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[100] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[101] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[102] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[103] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[104] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[105] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[106] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[107] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[108] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[109] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[110] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[111] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[112] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[113] Airbyte. “Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is, Benefits, & Use Cases.” https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-as-a-service
[114] Grand View Research. “Data As A Service Market Size, Share & Growth Report, 2030.” https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/data-as-a-service-market-report
[115] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[116] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas
[117] TIBCO. “What is Data as a Service (DaaS)?” https://www.tibco.com/glossary/what-is-data-as-a-service-daas