Author: everythingcryptoitclouds.com
Published: July 24, 2025
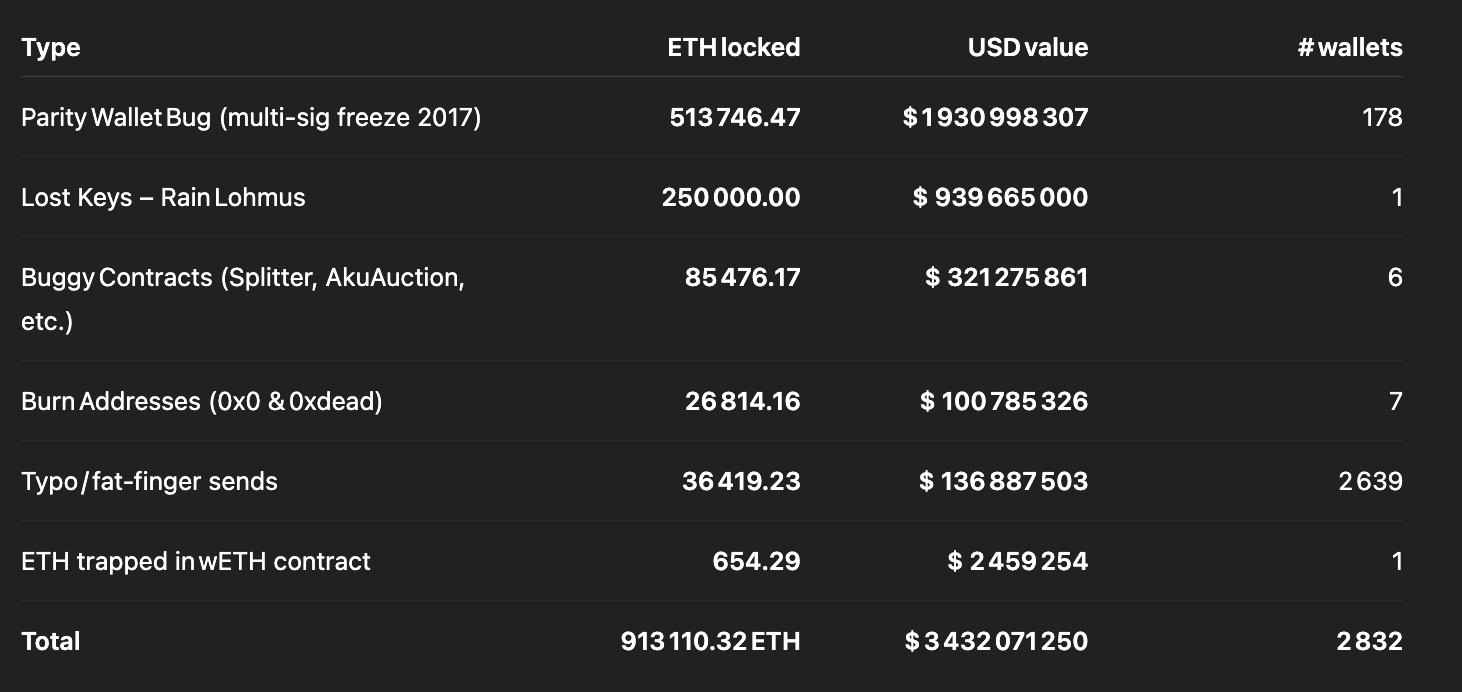
In the unforgiving digital landscape of blockchain technology, there exists a sobering reality that every cryptocurrency holder must confront: the permanent loss of digital assets. While Bitcoin’s lost coins have garnered significant attention over the years, Ethereum’s ecosystem presents an equally dramatic tale of irreversible losses that would make even the most seasoned investors pause. According to recent research by Coinbase’s head of product, Conor Grogan, over 913,111 ETH—worth approximately $3.4 billion at current market prices—has been lost forever due to user errors, smart contract bugs, and various technical mishaps [1].
This staggering figure represents more than just numbers on a blockchain explorer; it embodies the dreams, investments, and financial futures of countless individuals and organizations who fell victim to the unforgiving nature of decentralized technology. Unlike traditional banking systems where transactions can be reversed and funds can be recovered through customer service interventions, the blockchain operates under the principle of immutability—what is done cannot be undone.
The scale of this digital graveyard becomes even more profound when we consider that the $3.4 billion figure represents only the tip of the iceberg. As Grogan himself acknowledges, this amount “significantly undershoots the actual lost/inaccessible ETH amount” because it only covers instances where Ethereum is provably locked forever [2]. The calculation excludes the potentially massive amounts of ETH trapped behind lost private keys, forgotten Genesis wallets, and other forms of inaccessible storage that cannot be definitively quantified.
To put this loss into perspective, the 913,111 ETH represents approximately 0.76% of Ethereum’s current circulating supply of 120.7 million tokens [3]. When we include the 5.3 million ETH that has been intentionally burned through Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559 (EIP-1559) since 2021, the total amount of ETH removed from circulation reaches 6.2 million tokens, or roughly 5% of the total supply [4]. This deflationary pressure, while unintentional in the case of lost funds, has significant implications for Ethereum’s long-term economics and scarcity dynamics.
The phenomenon of lost ether is not merely a recent development but rather a persistent challenge that has plagued the Ethereum ecosystem since its inception. The research reveals that the amount of lost ETH has surged by 44% since March 2023, growing from 636,000 ETH to the current figure of over 913,000 ETH [5]. This acceleration in losses suggests that despite increased awareness and improved tooling, the fundamental risks associated with blockchain technology continue to claim victims at an alarming rate.
Understanding the mechanics of how ether becomes permanently lost requires delving into the technical architecture of the Ethereum blockchain and the various ways in which human error, software bugs, and malicious attacks can result in irreversible asset loss. Unlike traditional financial systems where regulatory frameworks and institutional safeguards provide multiple layers of protection, the decentralized nature of Ethereum places the entire burden of security and asset protection on individual users and smart contract developers.
The implications of this massive loss extend far beyond the immediate financial impact on affected individuals and organizations. Each lost ETH represents a reduction in the liquid supply available for trading, staking, and participation in the broader Ethereum ecosystem. This artificial scarcity, while potentially beneficial for remaining holders from a price perspective, also highlights the significant barriers to mainstream adoption that continue to plague cryptocurrency technology.
Moreover, the concentration of losses in specific categories—such as the 513,746 ETH trapped in Parity wallet bugs or the 60,000 ETH lost in the Quadriga exchange collapse—reveals systemic vulnerabilities in the infrastructure and tooling that supports the Ethereum ecosystem [6]. These incidents serve as stark reminders that the promise of decentralized finance comes with unprecedented risks that traditional financial systems have spent centuries learning to mitigate.
As we embark on this comprehensive exploration of lost ether, we will examine the various mechanisms through which ETH becomes permanently inaccessible, analyze the most significant loss events in Ethereum’s history, and investigate the evolving landscape of prevention strategies and recovery mechanisms. This analysis is not merely an academic exercise but a critical examination of the challenges that must be addressed for blockchain technology to achieve its transformative potential while protecting the assets and interests of its users.
The Anatomy of Lost Ether: Understanding How Digital Assets Disappear Forever
The permanent loss of Ethereum represents a multifaceted phenomenon that encompasses various technical, human, and systemic factors. To comprehend the full scope of this digital tragedy, we must examine the distinct categories through which ETH becomes irretrievably lost and the underlying mechanisms that make recovery impossible within the current blockchain paradigm.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: The Technical Achilles’ Heel
The largest single category of lost ether stems from vulnerabilities in smart contracts—self-executing programs that run on the Ethereum blockchain. These digital agreements, while revolutionary in their potential to automate complex financial transactions without intermediaries, have proven to be fertile ground for catastrophic losses when their code contains bugs or design flaws.
The most prominent example of this category is the Parity wallet incident, which has resulted in the permanent freezing of 513,746 ETH worth nearly $925 million at current prices [7]. This loss occurred not through a single event but through two separate incidents that highlighted the fragility of smart contract security. The first incident in July 2017 saw attackers exploit a vulnerability in Parity’s multisig wallet version 1.5+, resulting in the theft of 150,000 ETH worth approximately $30 million at the time [8].
However, it was the second incident in November 2017 that created the more devastating and permanent loss. In an attempt to fix the vulnerability from the first attack, Parity released an updated version of their multisig wallet contract. Unfortunately, this fix introduced a new vulnerability that was accidentally triggered by a GitHub user known as “devops199” [9]. This individual, apparently unaware of the consequences of their actions, called the “suicide” function on the library contract that served as the foundation for all Parity multisig wallets created after July 20, 2017.
The technical details of this incident reveal the subtle but catastrophic nature of smart contract vulnerabilities. The Parity multisig wallets were designed using a library pattern where multiple wallet contracts would delegate calls to a shared library contract containing the core functionality. When the library contract was destroyed through the suicide function, all dependent wallet contracts became permanently frozen, unable to execute any transactions including withdrawals [10]. The affected wallets contained funds belonging to various organizations and individuals, with the Web3 Foundation alone having 306,000 ETH trapped in this incident [11].
The Parity incident exemplifies a broader challenge in smart contract development: the tension between code efficiency and security. The library pattern used by Parity was intended to reduce gas costs and improve code maintainability by allowing multiple contracts to share common functionality. However, this architectural decision created a single point of failure that, when exploited, affected hundreds of wallets simultaneously.
Beyond Parity, the research identifies 85,476 ETH lost to various buggy contracts, representing $153.8 million in current value [12]. These losses span a wide range of contract types and failure modes, from decentralized exchange contracts with withdrawal bugs to token contracts with flawed transfer mechanisms. Each incident represents a unique combination of coding errors, insufficient testing, and the immutable nature of blockchain deployment that prevents post-deployment fixes.
The Akutars NFT collection provides another instructive example of how smart contract bugs can result in permanent losses. During the minting process for this non-fungible token collection, a bug in the contract code resulted in 11,500 ETH becoming permanently locked within the contract [13]. The funds were intended to be withdrawable by the project team after the minting process, but a coding error made this withdrawal impossible, effectively burning the ETH forever.
These incidents highlight a fundamental challenge in the Ethereum ecosystem: the irreversible nature of smart contract deployment. Unlike traditional software where bugs can be patched through updates, smart contracts deployed on Ethereum are immutable by design. While this immutability provides security benefits by preventing unauthorized modifications, it also means that any bugs present at deployment time become permanent features of the contract.
Human Error: The Persistent Vulnerability
While smart contract bugs represent the largest category of lost ether by value, human error constitutes the most diverse and persistent source of losses. The research identifies 12,619 ETH lost to typos alone, representing over $22.7 million in current value across 2,638 affected wallets [14]. This category encompasses a wide range of user mistakes, from simple transcription errors to fundamental misunderstandings of how Ethereum addresses work.
The most common form of human error involves mistakes in Ethereum address entry. Ethereum addresses are 42-character hexadecimal strings that begin with “0x” and are case-sensitive when using the optional checksum format. A single character error in an address can result in funds being sent to an uncontrolled address, effectively burning them forever. Unlike traditional banking systems where account numbers are validated and incorrect transfers can be reversed, the Ethereum blockchain executes all valid transactions irreversibly.
The prevalence of address-related errors has led to various mitigation strategies within the Ethereum ecosystem. The Ethereum Improvement Proposal 55 (EIP-55) introduced a checksum format that uses mixed case letters to help detect transcription errors [15]. However, adoption of this format is not universal, and many users continue to work with non-checksummed addresses that provide no error detection capabilities.
Another significant source of human error involves the misunderstanding of smart contract interactions. Many users have lost funds by sending ETH directly to token contracts or other smart contracts that are not designed to handle direct ETH transfers. When ETH is sent to a contract that lacks a payable fallback function or proper handling mechanisms, the funds become permanently trapped within the contract with no mechanism for retrieval.
The research also identifies 24,187 ETH that has been deliberately sent to burn addresses, representing $43.5 million in current value [16]. While some of these transactions may have been intentional burns for various purposes, many likely represent user errors where individuals mistakenly sent funds to known burn addresses. The most commonly used burn address is 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000, which is easily recognizable but apparently not universally understood as a destination that will permanently destroy any sent funds.
The psychological factors contributing to human error in cryptocurrency transactions cannot be understated. The irreversible nature of blockchain transactions creates a high-stress environment where users must be perfect in their execution of financial operations. Unlike traditional banking where customers can call customer service to reverse mistaken transactions, blockchain users bear the full responsibility for transaction accuracy with no safety net for errors.
Exchange Failures and Custodial Losses
The collapse of cryptocurrency exchanges represents another significant category of lost ether, with the Quadriga exchange serving as the most prominent example. Initially, Quadriga announced in June 2017 that they had lost 14 million CAD worth of Ethereum due to a smart contract error [17]. However, subsequent investigations revealed that this loss was part of a much larger pattern of mismanagement and potential fraud that ultimately resulted in the permanent loss of approximately 60,000 ETH [18].
The Quadriga case illustrates the risks associated with centralized custody of cryptocurrency assets. When users deposit funds on an exchange, they are essentially trusting the exchange operators to maintain proper security practices and financial controls. The death of Quadriga’s founder, Gerald Cotten, in December 2018 revealed that the exchange had been operating with significant security vulnerabilities, including the storage of private keys on a single individual’s encrypted laptop [19].
The investigation into Quadriga’s collapse revealed that Cotten had been using customer funds to cover trading losses totaling approximately $115 million [20]. This practice, known as commingling of funds, is prohibited in traditional financial services but was apparently common in the early cryptocurrency exchange industry due to lack of regulatory oversight and proper auditing procedures.
The Quadriga incident highlights the broader risks associated with centralized cryptocurrency services. While exchanges provide convenience and liquidity for cryptocurrency trading, they also represent single points of failure that can result in massive losses when they fail. The phrase “not your keys, not your coins” has become a rallying cry in the cryptocurrency community, emphasizing the importance of self-custody for long-term asset security.
Beyond Quadriga, numerous other exchange failures have contributed to the overall tally of lost ether. The Mt. Gox collapse, while primarily affecting Bitcoin, also resulted in the loss of various altcoins including early Ethereum holdings. More recent incidents, such as the FTX collapse, have demonstrated that exchange failures remain a persistent risk in the cryptocurrency ecosystem despite increased regulatory attention and improved security practices.
The DAO Hack: A Defining Moment in Ethereum History
No discussion of lost ether would be complete without examining The DAO hack of June 2016, an incident that not only resulted in significant financial losses but also fundamentally shaped the development trajectory of the Ethereum ecosystem. The Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) was an ambitious experiment in decentralized governance and investment, raising approximately $150 million worth of ETH through a token sale [21].
The DAO operated through smart contracts that allowed token holders to propose and vote on investment decisions. However, the contract code contained a critical vulnerability known as a reentrancy bug, which allowed an attacker to repeatedly withdraw funds from the contract before the balance was updated [22]. On June 17, 2016, an anonymous attacker exploited this vulnerability to drain approximately 3.6 million ETH, worth about $70 million at the time [23].
The DAO hack presented the Ethereum community with an unprecedented crisis. The attacker had not technically broken any rules of the blockchain protocol; they had simply exploited a vulnerability in a smart contract according to the code’s logic. This raised fundamental questions about the nature of smart contracts and whether “code is law” should be the ultimate principle governing blockchain-based systems.
The response to The DAO hack was highly controversial and ultimately led to a hard fork of the Ethereum blockchain. The majority of the Ethereum community supported a fork that would reverse the effects of the hack and return the stolen funds to their original owners. However, a minority faction argued that this intervention violated the immutability principles of blockchain technology and continued to support the original chain, which became known as Ethereum Classic [24].
While the hard fork successfully recovered the funds stolen in The DAO hack, it established a precedent that the Ethereum blockchain could be modified to reverse the effects of smart contract exploits under extreme circumstances. This precedent has been invoked in subsequent incidents, such as the Parity wallet freeze, but the Ethereum community has generally been reluctant to implement additional hard forks for fund recovery purposes.
The DAO incident serves as a watershed moment that highlighted both the potential and the risks of smart contract technology. It demonstrated that even well-funded and extensively reviewed smart contracts could contain critical vulnerabilities, and that the decentralized nature of blockchain governance could make it difficult to respond quickly to security incidents.
Technical Infrastructure Failures
Beyond user errors and smart contract bugs, the Ethereum ecosystem has also experienced losses due to failures in the technical infrastructure that supports the network. These incidents, while less common than other categories, have resulted in significant losses and highlight the complex interdependencies within the blockchain ecosystem.
One category of infrastructure failure involves issues with wallet software and key management systems. Early Ethereum wallets often had poor user interfaces and inadequate backup mechanisms, leading to situations where users could lose access to their funds due to software bugs or data corruption. The transition from the original Ethereum wallet software to more modern alternatives like MetaMask and hardware wallets has reduced but not eliminated these risks.
Another source of infrastructure-related losses involves issues with the Ethereum network itself during periods of high congestion or protocol upgrades. While the Ethereum protocol is designed to be robust against such issues, the complexity of the system means that edge cases and unexpected interactions can sometimes result in transaction failures or other problems that may lead to fund losses.
The research also identifies 654 ETH trapped in WETH (Wrapped Ethereum) contracts, representing $1.2 million in current value [25]. WETH is a tokenized version of ETH that allows it to be used in decentralized applications that require ERC-20 token interfaces. While WETH is generally considered safe and widely used, the trapped funds likely represent instances where users sent ETH directly to WETH contracts without properly calling the deposit function, or where bugs in WETH-related contracts prevented proper unwrapping of tokens.
These infrastructure-related losses underscore the importance of robust testing and quality assurance in the development of blockchain-related software and services. As the Ethereum ecosystem continues to evolve and mature, the focus on infrastructure reliability and user experience improvements becomes increasingly critical for preventing future losses.
Chronicles of Catastrophe: Major Historical Incidents That Shaped Ethereum’s Loss Landscape
The history of lost ether is punctuated by several major incidents that not only resulted in significant financial losses but also served as defining moments in the evolution of the Ethereum ecosystem. These events provide valuable insights into the various failure modes that can affect blockchain-based systems and the lessons learned from each catastrophe.
The Parity Multisig Saga: A Tale of Two Disasters
The Parity wallet incidents represent the most significant source of permanently lost ether in Ethereum’s history, with the story unfolding across two separate but related events that collectively demonstrate the cascading effects of smart contract vulnerabilities.
The First Strike: July 19, 2017
The initial Parity incident occurred on July 19, 2017, when an attacker exploited a vulnerability in the Parity multisig wallet contract version 1.5 and higher. The attack was sophisticated and targeted, focusing on three specific Ethereum Initial Coin Offering (ICO) projects: Aeternity, Edgeless, and Swarm City [26]. The attacker managed to steal approximately 150,000 ETH, worth around $30 million at the time, by exploiting a flaw in the wallet’s initialization process.
The technical details of this attack reveal the subtle nature of smart contract vulnerabilities. The Parity multisig wallet used a library pattern where the main wallet contract would delegate calls to a shared library contract containing the core functionality. However, the library contract itself could be initialized as if it were a regular wallet, allowing the attacker to become its owner and then use the wallet’s functionality to transfer funds from other wallets that relied on the same library [27].
The attack sequence was methodical and devastating. The attacker first identified vulnerable wallets by scanning the blockchain for contracts that used the affected Parity library. They then called the initialization function on the library contract to become its owner, followed by systematic draining of funds from the dependent wallets. The entire attack was completed within a matter of hours, demonstrating both the speed at which blockchain-based attacks can unfold and the difficulty of implementing real-time defensive measures.
The immediate response to this attack involved Parity releasing a security advisory and urging users to move their funds to secure wallets. However, the damage was already done for the affected projects. Aeternity lost approximately 37,000 ETH, Edgeless lost around 82,000 ETH, and Swarm City lost about 44,000 ETH [28]. These losses represented significant portions of these projects’ treasuries and had lasting impacts on their development and operations.
The Fatal Flaw: November 6, 2017
The second Parity incident, occurring on November 6, 2017, was even more devastating in its scope and permanence. In response to the July attack, Parity had released a new version of their multisig wallet that was intended to address the vulnerabilities that had been exploited. However, this fix introduced a new and more catastrophic vulnerability that would result in the permanent freezing of over 500,000 ETH.
The November incident was triggered not by a malicious attacker but by a GitHub user operating under the handle “devops199” who appeared to be experimenting with the Parity contract code [29]. This individual called the initWallet function on the library contract, making themselves the owner, and then immediately called the kill function, which executed the contract’s self-destruct mechanism.
The consequences of this action were immediate and irreversible. Because all Parity multisig wallets created after July 20, 2017, relied on the now-destroyed library contract, they became permanently frozen. Users could see their funds in the wallets but could not execute any transactions, including withdrawals. The affected wallets contained a total of 513,746 ETH, worth approximately $280 million at the time and over $900 million at current prices [30].
The technical architecture that enabled this catastrophic failure illustrates a fundamental tension in smart contract design between efficiency and security. The library pattern used by Parity was intended to reduce deployment costs and improve code maintainability by allowing multiple contracts to share common functionality. However, this design created a single point of failure that, when compromised, affected hundreds of wallets simultaneously.
Among the most significant victims of this incident was the Web3 Foundation, the organization behind the Polkadot blockchain project, which had 306,000 ETH frozen in affected wallets [31]. This loss represented a substantial portion of the foundation’s treasury and significantly impacted their ability to fund development activities. Other affected parties included various ICO projects, individual investors, and organizations that had chosen Parity’s multisig solution for its perceived security benefits.
The aftermath of the November incident sparked intense debate within the Ethereum community about potential recovery mechanisms. Parity and affected parties lobbied for a hard fork similar to the one that had been implemented to recover funds from The DAO hack. However, the community’s appetite for such interventions had diminished significantly since 2016, and the proposal for a recovery fork was ultimately rejected [32].
The Quadriga Collapse: When Centralization Meets Catastrophe
The collapse of QuadrigaCX, once Canada’s largest cryptocurrency exchange, represents a complex case study in the risks associated with centralized custody and the potential for both technical failures and fraudulent activity to result in permanent asset losses.
The Initial Technical Failure
Quadriga’s problems first became publicly apparent in June 2017 when the exchange announced that it had lost approximately 14 million CAD worth of Ethereum due to a smart contract error [33]. According to the exchange’s public statements, the loss occurred when they attempted to upgrade their Ethereum storage system and encountered a bug in the smart contract code that made the funds inaccessible.
At the time, this incident was treated as an unfortunate but isolated technical failure. Quadriga assured customers that the loss would not affect their operations and that they were working to improve their security procedures to prevent similar incidents. The exchange continued operating normally for over a year following this announcement, processing customer deposits and withdrawals without apparent difficulty.
However, subsequent investigations would reveal that this initial loss was likely part of a much larger pattern of mismanagement and potential fraud that had been ongoing for years. The smart contract error may have been genuine, but it occurred in the context of an exchange that was already experiencing significant financial difficulties due to other factors.
The Founder’s Death and the Unraveling
The true scope of Quadriga’s problems became apparent in December 2018 when the exchange’s founder and CEO, Gerald Cotten, died suddenly while traveling in India [34]. Cotten’s death initially appeared to be a tragic but straightforward event—a young entrepreneur who had succumbed to complications from Crohn’s disease while on his honeymoon.
However, Cotten’s death created an immediate crisis for Quadriga because he had apparently been the sole individual with access to the exchange’s cold storage wallets containing the majority of customer funds. According to his widow, Jennifer Robertson, Cotten had stored the private keys for these wallets on an encrypted laptop, and he had not shared the encryption passwords with anyone else [35].
The exchange filed for creditor protection in January 2019, claiming that approximately 190 million CAD worth of cryptocurrency was inaccessible due to Cotten’s death. This included not only Bitcoin but also significant amounts of Ethereum and other altcoins. The initial assumption was that this represented a tragic case of poor key management practices that had resulted in the permanent loss of customer funds.
The Investigation and Revelations
As investigators began examining Quadriga’s operations more closely, a much more disturbing picture emerged. The Ontario Securities Commission conducted a comprehensive review of the exchange’s activities and published their findings in April 2020 [36]. The investigation revealed that Quadriga had been operating as a Ponzi scheme for years, with Cotten using new customer deposits to pay withdrawal requests from existing customers.
The investigation found that Cotten had been conducting unauthorized trading activities using customer funds, resulting in losses of approximately 115 million CAD [37]. These trading losses were hidden from customers and covered up through various accounting manipulations and the use of new customer deposits. The exchange’s claimed cold storage reserves were largely fictitious, with most customer funds having been lost through Cotten’s trading activities long before his death.
The 60,000 ETH that appears in the lost ether statistics likely represents a combination of the initial smart contract error and funds that were lost through Cotten’s unauthorized trading activities. While some of these losses may be recoverable through bankruptcy proceedings, the complex nature of the fraud and the international jurisdictional issues involved make full recovery unlikely.
The Quadriga case highlights the risks associated with centralized cryptocurrency services and the importance of proper regulatory oversight. Unlike traditional financial institutions, which are subject to strict capital requirements and regular audits, early cryptocurrency exchanges operated with minimal oversight and often lacked basic financial controls.
The DAO Hack: Ethereum’s Existential Crisis
The DAO hack of June 2016 stands as perhaps the most consequential incident in Ethereum’s history, not only because of the immediate financial losses but also because of its lasting impact on the platform’s governance philosophy and technical development.
The Vision and the Vulnerability
The Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) was conceived as a revolutionary experiment in decentralized governance and investment. Launched in April 2016, The DAO raised approximately 12.7 million ETH (worth about $150 million at the time) through a token sale, making it one of the largest crowdfunding efforts in history [38]. The project aimed to create a decentralized venture capital fund where token holders could propose and vote on investment decisions without traditional intermediaries.
The DAO’s smart contract was complex, implementing sophisticated governance mechanisms that allowed for proposal submission, voting, and fund allocation. However, this complexity also created numerous potential attack vectors that were not fully understood or tested before deployment. The contract had undergone some security review, but the nascent state of smart contract auditing practices meant that critical vulnerabilities remained undetected.
The specific vulnerability that led to The DAO hack was a reentrancy bug in the contract’s withdrawal mechanism. When a user requested to withdraw their funds from The DAO, the contract would first send the ETH to the user’s address and then update the user’s balance in the contract’s internal accounting system. However, if the recipient address was itself a smart contract, it could call back into The DAO’s withdrawal function before the balance update occurred, allowing for multiple withdrawals of the same funds [39].
The Attack Unfolds
On June 17, 2016, an anonymous attacker began exploiting this vulnerability in a systematic and devastating manner. The attack was not a quick smash-and-grab operation but rather a methodical draining process that continued for several hours. The attacker deployed a malicious smart contract that would repeatedly call The DAO’s withdrawal function, each time extracting more ETH before the balance could be properly updated.
The Ethereum community watched in horror as The DAO’s balance steadily decreased throughout the day. Developers and security researchers quickly identified the nature of the attack and began working on potential countermeasures, but the decentralized nature of the blockchain meant that there was no central authority that could simply halt the attack in progress.
By the time the attack was complete, the attacker had drained approximately 3.6 million ETH from The DAO, representing about one-third of the total funds raised [40]. The stolen ETH was moved to a child DAO contract, where it would be subject to a 28-day holding period before the attacker could access it. This holding period provided a crucial window of opportunity for the Ethereum community to consider response options.
The Community Response and Hard Fork Decision
The DAO hack created an unprecedented crisis for the Ethereum community. The attack had not violated any rules of the Ethereum protocol itself; the attacker had simply exploited a vulnerability in a smart contract according to the code’s programmed logic. This raised fundamental questions about the principle of “code is law” and whether the Ethereum blockchain should be modified to reverse the effects of the hack.
The debate that followed was intense and divisive. Supporters of intervention argued that The DAO represented such a significant portion of the Ethereum ecosystem that its failure could undermine confidence in the entire platform. They also pointed out that the attack exploited a bug rather than a legitimate feature, making it morally justifiable to reverse its effects.
Opponents of intervention argued that modifying the blockchain to reverse the hack would violate the immutability principles that made blockchain technology valuable in the first place. They contended that smart contract bugs were a risk that users had accepted when participating in The DAO, and that bailing out failed projects would create moral hazard and undermine the credibility of the platform.
After extensive community discussion and debate, the Ethereum Foundation and core developers decided to implement a hard fork that would reverse the effects of The DAO hack. The fork was designed to move all ETH from The DAO and its child contracts to a recovery contract where original investors could withdraw their funds [41].
The Split and Ethereum Classic
While the hard fork had majority support within the Ethereum community, a significant minority opposed the intervention and continued to mine the original chain. This chain became known as Ethereum Classic (ETC), and it maintained the original transaction history including The DAO hack [42].
The existence of Ethereum Classic created a permanent reminder of the controversy surrounding The DAO hard fork. While Ethereum (ETH) became the dominant chain and continued to develop new features and improvements, Ethereum Classic maintained a more conservative approach focused on immutability and resistance to protocol changes.
The DAO incident and its aftermath had lasting effects on the Ethereum ecosystem. It demonstrated both the potential and the risks of smart contract technology, leading to improved development practices and security tools. It also established precedents for community governance and decision-making that continue to influence Ethereum’s development today.
Akutars and the NFT Minting Disaster
The Akutars incident of April 2022 represents a more recent example of how smart contract bugs can result in permanent fund losses, this time in the context of the non-fungible token (NFT) boom that characterized much of 2021 and 2022.
The Project and the Promise
Akutars was an NFT project created by artist Micah Johnson, featuring 15,000 unique digital collectibles. The project gained significant attention due to Johnson’s reputation as a former professional baseball player turned artist and the high-quality artwork featured in the collection. The NFT mint was structured as a Dutch auction, where the price would start high and gradually decrease until all tokens were sold.
The smart contract for the Akutars mint was designed to include several advanced features, including a refund mechanism for users who paid more than the final clearing price and a withdrawal function that would allow the project team to access the raised funds after the mint was complete. These features were intended to create a fair and transparent minting process that would benefit both collectors and the project creators.
The Fatal Flaw
However, the smart contract contained a critical bug in the interaction between its refund mechanism and withdrawal function. The contract was designed to track the total amount of refunds that needed to be paid out and prevent the project team from withdrawing funds until all refunds had been processed. Unfortunately, the logic for calculating the refund amount was flawed, creating a situation where the contract believed it owed more in refunds than it actually did.
When the mint concluded, the contract had raised approximately 11,539 ETH from the sale of the NFTs. However, due to the bug in the refund calculation, the contract’s internal accounting showed that it owed more in refunds than the total amount raised. This created a deadlock situation where neither refunds nor team withdrawals could be processed, effectively trapping all 11,539 ETH within the contract permanently [43].
The technical details of this bug illustrate the subtle ways in which smart contract logic can fail. The contract used a complex system of mappings and calculations to track individual user contributions and refund amounts. However, the developers failed to account for certain edge cases in the refund calculation, leading to an overflow condition that made the contract’s internal state inconsistent with reality.
The Aftermath and Lessons Learned
The Akutars incident was particularly tragic because it affected not only the project creators, who lost access to the funds they had legitimately raised, but also the NFT collectors who were unable to receive their promised refunds. The bug was discovered shortly after the mint concluded, but the immutable nature of smart contracts meant that no fix could be implemented.
Various attempts were made to recover the funds, including proposals for community-driven recovery mechanisms and potential protocol-level interventions. However, unlike The DAO hack, the Akutars incident did not generate sufficient community support for a hard fork or other extraordinary measures.
The incident highlighted the continued risks associated with smart contract development, even years after the early disasters like The DAO and Parity incidents. Despite the availability of better development tools, security auditing services, and educational resources, complex smart contracts continued to contain critical vulnerabilities that could result in permanent fund losses.
The Akutars case also demonstrated the particular risks associated with the NFT boom, where rapid development cycles and competitive pressure to launch projects quickly sometimes led to insufficient testing and security review. The incident served as a wake-up call for the NFT community about the importance of proper smart contract security practices.
Lessons from the Graveyard
These major incidents, while devastating for those directly affected, have provided valuable lessons that have shaped the development of the Ethereum ecosystem. Each disaster has contributed to improved development practices, better security tools, and enhanced user education about the risks associated with blockchain technology.
The Parity incidents led to widespread adoption of more rigorous smart contract auditing practices and the development of formal verification tools that can mathematically prove the correctness of contract code. The DAO hack established important precedents for community governance and highlighted the need for careful consideration of the trade-offs between intervention and immutability.
The Quadriga collapse reinforced the importance of proper key management and regulatory oversight for centralized cryptocurrency services. The Akutars incident demonstrated that smart contract risks persist even as the ecosystem matures and that continued vigilance is required in the development and deployment of complex contracts.
Despite these lessons, the continued growth in lost ether statistics suggests that the fundamental challenges of blockchain security remain unsolved. As the ecosystem continues to evolve and new use cases emerge, the potential for novel failure modes and unexpected vulnerabilities remains a persistent concern that requires ongoing attention and innovation to address.
Fortress of Digital Assets: Comprehensive Prevention Strategies and Security Best Practices
The sobering reality of permanently lost ether underscores the critical importance of implementing robust security measures and following established best practices when handling cryptocurrency assets. Unlike traditional financial systems where regulatory frameworks and institutional safeguards provide multiple layers of protection, the decentralized nature of Ethereum places the entire burden of security on individual users and developers. This section provides a comprehensive guide to protecting your digital assets from the various threats that have claimed billions of dollars worth of ETH throughout Ethereum’s history.
Wallet Security: Your First Line of Defense

The foundation of Ethereum security begins with proper wallet selection and management. The choice between different wallet types represents a fundamental trade-off between convenience and security, with each option presenting distinct advantages and risks that must be carefully considered based on your specific use case and risk tolerance.
Hardware Wallets: The Gold Standard for Long-Term Storage
Hardware wallets represent the most secure option for storing significant amounts of ETH, particularly for long-term holdings that are not frequently accessed. These devices store private keys in specialized secure hardware that is isolated from internet-connected computers, making them virtually immune to remote attacks and malware [44].
The two leading hardware wallet manufacturers, Ledger and Trezor, have established strong reputations for security and reliability within the cryptocurrency community. Ledger devices use a proprietary secure element chip that provides hardware-level protection for private keys, while Trezor devices use an open-source approach that allows for community security review and verification [45].
When using hardware wallets, several critical security practices must be followed to maintain their effectiveness. First, hardware wallets should only be purchased directly from the manufacturer or authorized resellers to avoid the risk of receiving compromised devices. There have been documented cases of attackers intercepting hardware wallets during shipping and modifying them to steal funds [46].
The setup process for hardware wallets requires careful attention to seed phrase generation and backup procedures. The seed phrase, typically consisting of 12 or 24 words, serves as the master key that can regenerate all private keys associated with the wallet. This phrase must be written down on paper and stored in multiple secure locations, as losing the seed phrase while the hardware device is damaged or lost will result in permanent fund loss [47].
Physical security of hardware wallets is equally important as their digital security features. The devices should be stored in secure locations when not in use, and users should be aware that physical access to a hardware wallet may allow sophisticated attackers to extract private keys through side-channel attacks or other advanced techniques [48].
Software Wallets: Balancing Convenience and Security
Software wallets, such as MetaMask, MyEtherWallet, and various mobile applications, provide greater convenience for frequent transactions but require additional security measures to protect against the broader attack surface of internet-connected devices. These wallets store private keys on the user’s device, making them vulnerable to malware, phishing attacks, and other forms of digital compromise.
The security of software wallets depends heavily on the security of the underlying device and operating system. Users should ensure that their computers and mobile devices are kept up to date with the latest security patches and are protected by reputable antivirus software. The use of dedicated devices or virtual machines for cryptocurrency activities can provide additional isolation from potential threats [49].
Browser-based wallets like MetaMask face particular security challenges due to their integration with web browsers, which are frequent targets for malicious attacks. Users should be extremely cautious about the websites they visit while their wallet is unlocked and should consider using separate browser profiles or dedicated browsers for cryptocurrency activities [50].
The backup and recovery procedures for software wallets are critical for preventing permanent fund loss. Like hardware wallets, software wallets typically use seed phrases for backup and recovery. These phrases should be stored securely offline and never entered into any digital device except when performing legitimate recovery operations [51].
Multi-Signature Wallets: Distributed Security Through Consensus
Multi-signature (multisig) wallets represent an advanced security approach that requires multiple private keys to authorize transactions, distributing the risk of fund loss across multiple parties or devices. While the Parity multisig incidents demonstrate that these wallets are not immune to smart contract vulnerabilities, properly implemented multisig solutions can provide significant security benefits for organizations and high-value individual holdings [52].
The most common multisig configurations include 2-of-3 setups, where any two of three authorized parties can approve transactions, and 3-of-5 setups for larger organizations. These configurations provide redundancy against the loss of individual keys while maintaining security against unauthorized access. The threshold should be chosen carefully to balance security against the risk of losing access due to unavailable signers [53].
Modern multisig implementations, such as Gnosis Safe, have learned from the failures of earlier solutions like Parity and implement more robust security practices. These include formal verification of smart contract code, extensive security auditing, and the use of battle-tested contract patterns that minimize the risk of critical vulnerabilities [54].
Transaction Security: Preventing Costly Mistakes
The irreversible nature of Ethereum transactions makes transaction security practices critically important for preventing permanent fund loss. Unlike traditional banking systems where transactions can be reversed or corrected, every Ethereum transaction must be executed with perfect accuracy to avoid irreversible mistakes.
Address Verification: The Critical First Step
Address verification represents the most fundamental aspect of transaction security, as sending funds to an incorrect address is one of the most common causes of permanent loss. Ethereum addresses are 42-character hexadecimal strings that are not human-readable, making them prone to transcription errors and other mistakes [55].
The Ethereum community has developed several tools and practices to reduce the risk of address-related errors. The EIP-55 checksum format uses mixed-case letters to encode error detection information directly into the address, allowing wallets to detect many common transcription errors [56]. However, not all wallets and services support checksum validation, and users should verify that their chosen tools implement this protection.
Visual verification tools, such as identicons and address avatars, provide additional protection against address errors by generating unique visual representations of addresses that are easier for humans to verify than long hexadecimal strings. Many wallets display these visual identifiers alongside addresses to help users confirm that they are sending funds to the intended recipient [57].
For high-value transactions, the practice of sending small test amounts before transferring larger sums provides an additional layer of protection. While this approach incurs additional transaction fees, the cost is minimal compared to the potential loss from sending funds to an incorrect address [58].
Smart Contract Interaction Safety
Interacting with smart contracts presents additional security challenges beyond simple ETH transfers, as users must understand the implications of the contract functions they are calling and the permissions they are granting. The complexity of modern DeFi protocols and other smart contract applications makes it increasingly difficult for users to fully understand the risks associated with their transactions.
Transaction simulation tools, such as those provided by Tenderly and other services, allow users to preview the effects of their transactions before execution. These tools can help identify potential issues such as failed transactions, unexpected token approvals, or interactions with malicious contracts [59].
The practice of limiting token approvals to specific amounts rather than granting unlimited permissions can help reduce the impact of smart contract vulnerabilities or malicious behavior. Many DeFi protocols request unlimited token approvals for convenience, but users should consider the security implications of granting such broad permissions [60].
Regular review and revocation of token approvals is an important maintenance practice that many users overlook. Services like Revoke.cash allow users to view and revoke previously granted token approvals, reducing the ongoing risk from contracts that may have been compromised or are no longer trusted [61].
Exchange and Service Security: Minimizing Custodial Risks
While self-custody represents the most secure approach for long-term cryptocurrency storage, many users rely on exchanges and other custodial services for trading and convenience. The Quadriga incident and numerous other exchange failures demonstrate the risks associated with custodial services, but proper practices can help minimize these risks.
Exchange Selection Criteria
The selection of cryptocurrency exchanges should be based on multiple security and reliability factors rather than simply choosing the platform with the lowest fees or most convenient features. Established exchanges with strong regulatory compliance, transparent operations, and robust security practices generally present lower risks than newer or less regulated alternatives [62].
Regulatory compliance serves as an important indicator of exchange reliability, as regulated exchanges are subject to capital requirements, regular audits, and other oversight mechanisms that reduce the risk of fraud or mismanagement. Exchanges operating in jurisdictions with strong financial regulations, such as the United States, European Union, and Japan, generally provide better protection for customer funds [63].
Security practices such as cold storage of customer funds, regular security audits, and bug bounty programs indicate that an exchange takes security seriously. Exchanges should be transparent about their security practices and should provide regular proof-of-reserves reports that demonstrate their ability to meet customer withdrawal demands [64].
Minimizing Exchange Exposure
Even when using reputable exchanges, users should minimize their exposure to custodial risks by following the principle of “not your keys, not your coins.” This means keeping only the minimum amount necessary for active trading on exchanges and regularly withdrawing funds to self-custody wallets [65].
The practice of dollar-cost averaging withdrawals can help reduce the impact of exchange failures by ensuring that funds are not concentrated on a single platform at any given time. Users who regularly trade should establish withdrawal schedules that balance convenience against security risks [66].
Two-factor authentication (2FA) should be enabled on all exchange accounts, preferably using hardware-based authenticators rather than SMS-based systems that are vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks. Withdrawal whitelisting, where available, provides additional protection by restricting withdrawals to pre-approved addresses [67].
Smart Contract Security: Due Diligence for Developers and Users
The numerous smart contract vulnerabilities that have resulted in permanent fund losses highlight the critical importance of security practices for both developers creating contracts and users interacting with them. The immutable nature of deployed contracts means that security must be built in from the beginning rather than added as an afterthought.
Development Best Practices
Smart contract development requires adherence to established security patterns and extensive testing to identify potential vulnerabilities before deployment. The use of well-tested libraries and frameworks, such as OpenZeppelin’s contract library, can help reduce the risk of introducing common vulnerabilities [68].
Formal verification techniques, which use mathematical proofs to verify the correctness of contract code, represent the gold standard for smart contract security. While formal verification is not practical for all contracts due to complexity and cost considerations, it should be considered for high-value contracts that will hold significant amounts of funds [69].
Security auditing by reputable firms provides an additional layer of protection against contract vulnerabilities. Multiple independent audits can help identify issues that might be missed by a single review, and the audit process should include both automated analysis tools and manual code review by experienced security professionals [70].
User Due Diligence
Users interacting with smart contracts should perform appropriate due diligence to understand the risks associated with the contracts they are using. This includes reviewing audit reports, understanding the contract’s functionality, and assessing the reputation and track record of the development team [71].
The age and usage history of smart contracts provide important indicators of their reliability. Contracts that have been deployed for extended periods and have processed significant transaction volumes without issues are generally safer than newly deployed contracts that have not been battle-tested [72].
Community sentiment and expert opinions can provide valuable insights into the security and reliability of smart contracts. Platforms like DeFiSafety and other rating services provide systematic evaluations of DeFi protocols and other smart contract applications [73].
Backup and Recovery: Preparing for the Unexpected
Comprehensive backup and recovery planning is essential for protecting against the various ways that access to cryptocurrency funds can be lost. Unlike traditional financial accounts where customer service can help recover access, cryptocurrency users must be prepared to handle recovery scenarios independently.
Seed Phrase Management
The secure storage and management of seed phrases represents the most critical aspect of cryptocurrency backup and recovery. Seed phrases should be written down on paper or engraved on metal plates that can withstand fire, water, and other environmental hazards. Digital storage of seed phrases should be avoided due to the risk of malware and other digital threats [74].
Multiple copies of seed phrases should be stored in geographically distributed locations to protect against localized disasters such as fires or floods. However, the number of copies should be limited to reduce the risk of unauthorized access, and each storage location should be secured against physical intrusion [75].
The use of passphrases (also known as the 25th word) can provide additional security for seed phrases by adding an extra layer of protection that is not written down with the seed phrase itself. However, users must be careful not to forget their passphrases, as this will result in permanent fund loss even if the seed phrase is recovered [76].
Estate Planning and Inheritance
The permanent nature of cryptocurrency losses makes estate planning particularly important for cryptocurrency holders. Without proper planning, cryptocurrency assets may become permanently inaccessible upon the holder’s death or incapacitation, effectively removing them from circulation forever [77].
Various approaches to cryptocurrency inheritance have been developed, ranging from simple sharing of seed phrases with trusted family members to more sophisticated solutions involving multi-signature wallets and time-locked contracts. The chosen approach should balance security against the risk of permanent loss due to the unavailability of the holder [78].
Professional estate planning services that specialize in cryptocurrency assets can help develop comprehensive inheritance plans that account for the unique challenges of digital asset management. These services can help structure inheritance mechanisms that provide appropriate security while ensuring that beneficiaries can access funds when needed [79].
Emerging Security Technologies and Future Developments
The Ethereum ecosystem continues to evolve with new security technologies and approaches that aim to address the fundamental challenges that have led to billions of dollars in lost funds. While these developments show promise, they also introduce new complexities and potential failure modes that must be carefully considered.
Account Abstraction and Social Recovery
Account abstraction, formalized in EIP-4337, represents a significant evolution in Ethereum wallet architecture that could help address many of the security challenges that have led to fund losses. This technology allows for more flexible wallet designs that can implement features like social recovery, spending limits, and other security mechanisms at the protocol level [80].
Social recovery mechanisms allow users to designate trusted contacts who can help recover access to funds if the primary authentication method is lost. This approach provides a middle ground between the security of self-custody and the convenience of custodial services, potentially reducing the risk of permanent fund loss due to lost private keys [81].
Hardware Security Modules and Institutional Solutions
The development of more sophisticated hardware security modules (HSMs) and institutional custody solutions provides additional options for securing large amounts of cryptocurrency. These solutions often combine the security benefits of hardware-based key storage with the convenience and reliability features required by institutional users [82].
Multi-party computation (MPC) technology allows for the distribution of private key material across multiple parties or devices without any single party having access to the complete key. This approach can provide security benefits similar to multi-signature wallets while avoiding some of the smart contract risks that have affected traditional multisig solutions [83].
Regulatory and Insurance Developments
The development of regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrency custody and the emergence of cryptocurrency insurance products provide additional layers of protection for users and institutions. While these developments do not eliminate the fundamental risks associated with cryptocurrency, they can help provide recourse in cases of loss due to custodial failures or other covered events [84].
The maturation of the cryptocurrency insurance market has led to the development of more sophisticated coverage options that can protect against various types of losses, including exchange failures, custody errors, and certain types of smart contract vulnerabilities. However, users should carefully review policy terms to understand what is and is not covered [85].
The Path Forward: Building a More Secure Ecosystem
The billions of dollars in permanently lost ether serve as a stark reminder of the challenges that must be overcome for cryptocurrency to achieve mainstream adoption. While the decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain technology provides significant benefits, it also places unprecedented responsibility on users and developers to implement and maintain proper security practices.
The continued development of better tools, educational resources, and security technologies offers hope for reducing future losses, but the fundamental trade-offs between security, convenience, and decentralization will likely persist. Users must remain vigilant and informed about the risks associated with cryptocurrency, while developers must continue to prioritize security in the design and implementation of new systems and applications.
The lessons learned from each major loss incident have contributed to the overall security posture of the Ethereum ecosystem, but the continued growth in lost funds suggests that more work remains to be done. The path forward requires continued innovation in security technologies, improved user education, and the development of more robust and user-friendly tools that can help protect users from the various threats that have claimed so many digital assets throughout Ethereum’s history.
The Recovery Paradox: Exploring Options and Limitations in Ethereum Asset Recovery
The permanent nature of blockchain transactions creates a fundamental paradox in cryptocurrency recovery: while the technology’s immutability provides security and trust, it also makes recovery from errors and attacks extremely difficult or impossible. This section examines the various recovery methods that have been attempted or proposed for lost ether, their limitations, and the ongoing debate about the appropriate balance between immutability and user protection.
Technical Recovery Approaches
Hard Forks: The Nuclear Option
Hard forks represent the most dramatic form of recovery mechanism available in blockchain systems, involving changes to the protocol rules that can effectively reverse or modify historical transactions. The Ethereum community has used this approach only once, in response to The DAO hack of 2016, and the controversy surrounding that decision continues to influence discussions about recovery mechanisms today [86].
The DAO hard fork was implemented through a coordinated effort by the Ethereum Foundation and core developers, who created a new version of the Ethereum client software that would redirect funds from The DAO and its child contracts to a recovery contract. Users who supported the fork upgraded their software, while those who opposed it continued running the original version, ultimately creating the Ethereum Classic split [87].
The technical implementation of the DAO hard fork was relatively straightforward because it involved modifying the state of specific contracts at a predetermined block height. However, the social and political challenges of achieving consensus for the fork were immense, requiring extensive community discussion and debate about the appropriate response to the attack [88].
Subsequent proposals for hard forks to recover lost funds, such as the EIP-999 proposal to restore the Parity multisig library contract, have been rejected by the Ethereum community. The rejection of EIP-999 reflected a shift in community sentiment away from interventionist approaches and toward acceptance of immutability as a fundamental principle of the platform [89].
The practical challenges of implementing recovery hard forks have grown significantly as the Ethereum ecosystem has matured. The increased number of stakeholders, the complexity of the network, and the existence of numerous derivative projects and layer-2 solutions make coordinated changes much more difficult to implement than they were in Ethereum’s early days [90].
Smart Contract-Based Recovery Mechanisms
Various proposals have been made for smart contract-based recovery mechanisms that could help users recover lost funds without requiring protocol-level changes. These approaches typically involve the creation of specialized contracts that can implement recovery logic for specific types of losses.
One proposed approach involves the creation of “recovery tokens” that would be distributed to holders of lost funds at a 1:1 ratio with their lost ETH. These tokens could potentially be traded or used in DeFi applications, providing some economic value to holders of otherwise worthless claims [91]. However, the practical implementation of such systems faces significant challenges in terms of verification, governance, and economic sustainability.
Time-locked recovery mechanisms represent another approach that could be built into smart contracts to provide recovery options for users who lose access to their funds. These systems could allow users to designate recovery addresses that would gain access to funds after a specified time period if the primary owner does not interact with the contract [92].
Social recovery systems, which are being implemented in some modern wallet designs, allow users to designate trusted contacts who can help recover access to funds through a consensus mechanism. While these systems show promise for preventing future losses, they cannot help recover funds that are already lost in existing contracts [93].
Professional Recovery Services
The cryptocurrency industry has spawned a specialized sector of professional recovery services that attempt to help users regain access to lost funds. These services employ various techniques ranging from password cracking to blockchain analysis, with varying degrees of success depending on the specific circumstances of each case [94].
Password recovery services, such as those offered by companies like KeychainX and Wallet Recovery Services, specialize in helping users who have forgotten passwords or passphrases for encrypted wallet files. These services use sophisticated brute-force techniques and social engineering to reconstruct likely passwords based on information provided by the user [95].
The success rates for password recovery services vary significantly depending on the strength of the original password and the amount of information the user can provide about their likely password choices. Services typically charge a percentage of recovered funds, with rates ranging from 10% to 20% of the total recovery amount [96].
Blockchain analysis services can sometimes help trace lost funds and identify potential recovery opportunities, particularly in cases involving exchange failures or other custodial losses. However, these services are generally ineffective for funds lost due to smart contract bugs or user errors that result in funds being sent to uncontrolled addresses [97].
Legal and Regulatory Recovery Mechanisms
Bankruptcy and Insolvency Proceedings
Traditional legal mechanisms such as bankruptcy and insolvency proceedings can sometimes provide recovery options for cryptocurrency losses, particularly in cases involving failed exchanges or other custodial services. The Quadriga bankruptcy proceedings, while ultimately unsuccessful in recovering most customer funds, demonstrate both the potential and limitations of legal recovery mechanisms [98].
The complexity of cryptocurrency assets creates significant challenges for traditional bankruptcy proceedings. Courts must grapple with questions about the classification of different types of digital assets, the valuation of volatile cryptocurrencies, and the technical challenges of actually recovering and distributing digital assets to creditors [99].
International jurisdictional issues further complicate legal recovery efforts, as cryptocurrency businesses often operate across multiple countries with different legal frameworks. The global nature of cryptocurrency markets means that assets may be held in jurisdictions that do not recognize or enforce judgments from other countries [100].
Regulatory Intervention and Consumer Protection
The development of regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrency businesses has created new avenues for consumer protection and potential recovery mechanisms. Regulatory agencies in various jurisdictions have begun implementing requirements for customer fund segregation, insurance coverage, and other protections that could help prevent or mitigate losses [101].
The European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation and similar frameworks in other jurisdictions establish requirements for cryptocurrency service providers that could help reduce the risk of custodial losses. However, these regulations typically do not provide retroactive protection for losses that occurred before their implementation [102].
Insurance requirements for cryptocurrency businesses represent another regulatory approach that could provide recovery options for certain types of losses. However, the nascent state of the cryptocurrency insurance market means that coverage is often limited and expensive, with many exclusions for common types of losses [103].
The Economics of Lost Ether: Market Implications and Deflationary Effects
The permanent loss of over 913,000 ETH represents more than just individual tragedies; it has significant implications for the broader Ethereum ecosystem and the economics of the ETH token itself. Understanding these economic effects is crucial for assessing the long-term impact of lost funds on the network and its participants.
Supply Reduction and Scarcity Dynamics
The permanent removal of ETH from circulation through various loss mechanisms creates artificial scarcity that can have significant effects on the token’s value and market dynamics. Unlike traditional currencies where lost or destroyed money can be replaced by central banks, lost cryptocurrency is permanently removed from the total supply [104].
The 913,000 ETH currently identified as permanently lost represents approximately 0.76% of the current circulating supply, but this figure likely understates the true extent of lost funds. When combined with the 5.3 million ETH burned through EIP-1559 since 2021, the total reduction in available supply reaches approximately 5% of the total ETH supply [105].
This supply reduction has deflationary effects that benefit remaining ETH holders by increasing the scarcity of the remaining tokens. However, the uneven distribution of losses means that the benefits are not equally shared among all participants in the ecosystem. Large institutional holders with sophisticated security practices are less likely to lose funds than individual users with limited technical expertise [106].
The concentration of losses in specific categories, such as the Parity multisig incident, also creates uneven effects across different segments of the Ethereum ecosystem. The Web3 Foundation’s loss of 306,000 ETH, for example, has had lasting impacts on the development of the Polkadot ecosystem and related projects [107].
Market Efficiency and Price Discovery
The permanent loss of ETH affects market efficiency and price discovery mechanisms by removing tokens from active trading and circulation. Lost funds cannot respond to market signals or participate in price discovery, potentially leading to increased volatility and reduced market liquidity [108].
The psychological effects of known lost funds on market participants can also influence trading behavior and price formation. The knowledge that significant amounts of ETH are permanently lost may create a perception of increased scarcity that affects investor behavior and valuation models [109].
However, the impact of lost funds on market dynamics is complicated by the fact that many lost funds were already inactive before being lost. Funds held in long-term storage or forgotten wallets may have had minimal impact on active trading markets even before becoming permanently inaccessible [110].
Network Security and Staking Implications
The transition of Ethereum to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism through “The Merge” in September 2022 has created new implications for lost ETH, as the network’s security now depends on the amount of ETH staked by validators rather than computational power [111].
Lost ETH cannot be staked to secure the network, effectively reducing the total amount of ETH available for staking and potentially affecting the network’s security properties. However, the impact of this reduction is likely minimal given the large amount of ETH that remains available for staking [112].
The staking rewards mechanism in proof-of-stake Ethereum creates ongoing incentives for ETH holders to actively participate in network security, potentially reducing the likelihood of funds becoming lost through neglect or forgotten storage. However, staking also introduces new risks, such as slashing penalties for validator misbehavior [113].
Innovation and Development Funding
The loss of significant amounts of ETH by organizations and projects has had direct impacts on innovation and development within the Ethereum ecosystem. The Web3 Foundation’s loss of 306,000 ETH in the Parity incident, for example, significantly affected their ability to fund development of the Polkadot ecosystem [114].
Similarly, the various ICO projects that lost funds in smart contract bugs and exchange failures have had reduced resources available for development and operations. These losses have contributed to the failure of some projects and have reduced the overall level of innovation and experimentation within the ecosystem [115].
The concentration of losses among early adopters and technically sophisticated users may have disproportionately affected the most innovative and experimental segments of the Ethereum community. These users were often the first to adopt new technologies and participate in experimental projects, making them more vulnerable to the various failure modes that have resulted in permanent losses [116].
Future Implications and Systemic Risks
Scaling and Layer-2 Considerations
The development of layer-2 scaling solutions and other advanced Ethereum technologies introduces new potential sources of fund loss while also providing opportunities for improved security and recovery mechanisms. Layer-2 solutions such as Optimism, Arbitrum, and Polygon operate their own smart contract systems that may contain vulnerabilities similar to those that have affected the main Ethereum network [117].
The bridging mechanisms that allow funds to move between Ethereum and layer-2 networks represent new potential points of failure that could result in significant losses. Several high-profile bridge hacks have already demonstrated the risks associated with these systems, and the increasing complexity of multi-chain interactions may create new categories of permanent loss [118].
However, layer-2 solutions also provide opportunities for implementing more sophisticated recovery mechanisms and security features that may not be practical on the main Ethereum network due to gas costs and other constraints. Some layer-2 systems are experimenting with features like transaction reversibility windows and enhanced security monitoring that could help prevent or mitigate losses [119].
Institutional Adoption and Custody Solutions
The increasing institutional adoption of Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies is driving the development of more sophisticated custody solutions and security practices that may help reduce future losses. Institutional custody providers typically implement multiple layers of security and redundancy that can help prevent the types of losses that have affected individual users and smaller organizations [120].
However, institutional adoption also creates new systemic risks, as the failure of a major custody provider or institutional holder could result in losses that dwarf the individual incidents that have occurred to date. The concentration of large amounts of ETH in institutional custody solutions creates new single points of failure that could have significant impacts on the broader ecosystem [121].
The development of regulatory frameworks for institutional cryptocurrency custody is helping to establish minimum standards for security and risk management, but the rapidly evolving nature of the technology means that regulations often lag behind the latest developments and potential risks [122].
Long-Term Sustainability and User Experience
The continued growth in lost ETH raises questions about the long-term sustainability of systems that place such high security burdens on individual users. While the principle of self-custody provides important benefits in terms of censorship resistance and financial sovereignty, the practical challenges of secure key management may limit mainstream adoption [123].
The development of more user-friendly security solutions, such as social recovery wallets and hardware security modules, represents important progress toward making cryptocurrency more accessible to mainstream users. However, these solutions often involve trade-offs between security and convenience that must be carefully balanced [124].
The ongoing evolution of user interface design and security practices in the cryptocurrency space suggests that future systems may be able to provide better protection against the types of losses that have occurred historically. However, the fundamental challenges of balancing security, usability, and decentralization are likely to persist as the ecosystem continues to evolve [125].
Conclusion: Lessons from the Digital Graveyard
The $3.4 billion worth of permanently lost ether represents more than just a statistical curiosity; it embodies the fundamental challenges and trade-offs inherent in decentralized financial systems. Each lost ETH tells a story of human error, technical failure, or malicious attack that highlights the unforgiving nature of blockchain technology and the immense responsibility placed on users and developers in this new financial paradigm.
The analysis of lost ether reveals several critical insights that extend far beyond the immediate financial impact on affected individuals and organizations. First, the diversity of loss mechanisms—from smart contract bugs to user errors to exchange failures—demonstrates that no single security measure or approach can provide complete protection against all potential threats. The Ethereum ecosystem’s complexity creates multiple attack vectors and failure modes that require comprehensive and layered security approaches.
Second, the concentration of losses in specific incidents, such as the Parity multisig freeze and The DAO hack, reveals the systemic risks that can emerge from widely-used infrastructure and the cascading effects that can result from single points of failure. These incidents have shaped the development of the Ethereum ecosystem and influenced the design of subsequent systems and protocols.
Third, the persistent growth in lost funds despite increased awareness and improved tooling suggests that the fundamental challenges of blockchain security remain unsolved. The 44% increase in lost ETH since March 2023 indicates that new users and applications continue to fall victim to the same categories of errors and vulnerabilities that have plagued the ecosystem since its inception.
The economic implications of lost ether extend beyond the immediate impact on affected parties to influence the broader dynamics of the Ethereum ecosystem. The artificial scarcity created by permanently lost funds affects token economics, market dynamics, and network security in ways that are still being understood and analyzed. The deflationary pressure from lost funds, combined with the intentional burning of ETH through EIP-1559, creates complex economic dynamics that will continue to evolve as the ecosystem matures.
The prevention strategies and security best practices outlined in this analysis represent the current state of knowledge about protecting cryptocurrency assets, but they also highlight the significant burden placed on users to maintain perfect security practices in an unforgiving environment. The development of more user-friendly security solutions and the maturation of institutional custody services offer hope for reducing future losses, but the fundamental trade-offs between security, convenience, and decentralization will likely persist.
The recovery mechanisms explored in this analysis demonstrate both the potential and limitations of various approaches to addressing permanent fund loss. While technical solutions such as hard forks and smart contract-based recovery systems offer theoretical possibilities for fund recovery, the practical and political challenges of implementing such solutions have proven to be significant barriers. The rejection of recovery proposals like EIP-999 reflects the Ethereum community’s commitment to immutability principles, even at the cost of accepting permanent losses.
Looking forward, the continued evolution of the Ethereum ecosystem presents both new opportunities and new risks for fund security. The development of layer-2 scaling solutions, account abstraction, and other advanced technologies may provide new tools for preventing and mitigating losses, but they also introduce new complexities and potential failure modes that must be carefully managed.
The institutional adoption of Ethereum and the development of regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrency custody represent important developments that may help reduce certain categories of losses while potentially introducing new systemic risks. The balance between innovation and security will continue to be a central challenge as the ecosystem evolves and matures.
Perhaps most importantly, the story of lost ether serves as a reminder that the promise of decentralized finance comes with unprecedented responsibilities and risks. The elimination of traditional financial intermediaries and safety nets places the burden of security and asset protection directly on users and developers, requiring a level of technical sophistication and security awareness that may be challenging for mainstream adoption.
The lessons learned from each major loss incident have contributed to the overall security posture of the Ethereum ecosystem, but the continued growth in lost funds suggests that more work remains to be done. The path forward requires continued innovation in security technologies, improved user education, and the development of more robust and user-friendly tools that can help protect users from the various threats that have claimed so many digital assets throughout Ethereum’s history.
As the Ethereum ecosystem continues to evolve and mature, the challenge of balancing the benefits of decentralization with the need for user protection will remain a central concern. The billions of dollars in lost ether serve as a sobering reminder of the stakes involved and the importance of continued vigilance and innovation in the pursuit of a more secure and accessible decentralized financial system.
The digital graveyard of lost ether will likely continue to grow as new users enter the ecosystem and new technologies introduce novel failure modes. However, the lessons learned from past losses and the ongoing development of better security practices and tools offer hope that future losses can be minimized while preserving the fundamental benefits that make decentralized finance revolutionary.
In the end, the story of lost ether is not just about the funds that have been permanently lost, but about the ongoing evolution of a financial system that places unprecedented power and responsibility in the hands of its users. The challenge for the Ethereum community and the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem is to continue innovating and improving while learning from the mistakes and tragedies that have marked the path to this new financial frontier.
References
[1] Cointelegraph. (2025, July 21). “Human Error Causes $3.4B Ether Loss, Says Coinbase Exec.” https://cointelegraph.com/news/3-4b-ether-lost-forever-user-error-coinbase-conor-grogan
[2] GitHub – jconorgrogan/Lost-ETH. (2025). “Compilation of Ethereum typos, user errors, and buggy contracts.” https://github.com/jconorgrogan/Lost-ETH
[3] TradingView. (2025, July 21). “Ether lost forever hits $3.4B due to user error, Coinbase exec warns.” https://www.tradingview.com/news/cointelegraph:43025d7d6094b:0-ether-lost-forever-hits-3-4b-due-to-user-error-coinbase-exec-warns/
[4] Ethereum.org. (2024). “Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559 (EIP-1559).” https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/gas/#eip-1559
[5] The Block. (2023, March 21). “Over $1 billion of ether has been lost forever due to bugs and human error.” https://www.theblock.co/post/221453/over-1-billion-of-ether-lost-forever-bugs-human-error
[6] Digital Watch Observatory. (2025, July 23). “Over $3 billion of Ethereum lost forever.” https://dig.watch/updates/over-3-billion-of-ethereum-lost-forever
[7] CNBC. (2017, November 8). “‘Accidental’ bug froze $280 million worth of ether in Parity wallet.” https://www.cnbc.com/2017/11/08/accidental-bug-may-have-frozen-280-worth-of-ether-on-parity-wallet.html
[8] OpenZeppelin Blog. (2017, July 19). “The Parity Wallet Hack Explained.” https://blog.openzeppelin.com/on-the-parity-wallet-multisig-hack-405a8c12e8f7
[9] CCN. (2021, March 4). “‘I Accidentally Killed It’: Parity Wallet Bug Locks $150 Million in Ether.” https://www.ccn.com/i-accidentally-killed-it-parity-wallet-bug-locks-150-million-in-ether/
[10] BBC. (2017, November 9). “Code bug freezes $150m of Ethereum crypto-cash.” https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-41928147
[11] The Guardian. (2017, November 8). “‘$300m in cryptocurrency’ accidentally lost forever due to bug.” https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2017/nov/08/cryptocurrency-300m-dollars-stolen-bug-ether
[12] Coinspeaker. (2025, July 21). “Lost Ether Supply Reaches Over 913000 ETH, Worth Billions.” https://www.coinspeaker.com/lost-ether-supply-reaches-over-913000-eth-worth-billions/
[13] Ainvest. (2025, July 22). “Ethereum Faces $3.4 Billion Loss Due to User Errors and Technical Bugs.” https://www.ainvest.com/news/ethereum-news-today-ethereum-faces-3-4-billion-loss-due-user-errors-technical-bugs-2507/
[14] Medium – Consensys. (2018, March 9). “Over 12000 Ether Are Lost Forever Due to Typos.” https://medium.com/consensys-media/over-12-000-ether-are-lost-forever-due-to-typos-f6ccc35432f8
[15] Ethereum Improvement Proposals. (2016). “EIP-55: Mixed-case checksum address encoding.” https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-55
[16] Ethereum Stack Exchange. (2017, September 5). “How can I reverse or cancel a transaction or recover lost ethers?” https://ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/25866/how-can-i-reverse-or-cancel-a-transaction-or-recover-lost-ethers
[17] Wikipedia. “Quadriga (company).” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quadriga_(company)
[18] Norton Rose Fulbright. “Quadriga bankruptcy: C$190 million may have turned into digital dust.” https://www.nortonrosefulbright.com/en/knowledge/publications/168bc350/quadriga-bankruptcy
[19] CNN. (2019, February 5). “Quadriga CEO Gerald Cotten dies, leaving $145 million of cryptocurrency inaccessible.” https://www.cnn.com/2019/02/05/tech/quadriga-gerald-cotten-cryptocurrency
[20] Ontario Securities Commission. (2020, April 14). “QuadrigaCX: A Review by Staff of the Ontario Securities Commission.” https://www.osc.gov.on.ca/quadrigacxreport/
[21] Gemini Cryptopedia. “What Was the DAO Hack?” https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/the-dao-hack-makerdao
[22] Chainlink Blog. (2022, August 31). “Reentrancy Attacks and The DAO Hack Explained.” https://blog.chain.link/reentrancy-attacks-and-the-dao-hack/
[23] Wikipedia. “The DAO.” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_DAO
[24] CoinDesk. (2023, May 9). “CoinDesk Turns 10: 2016 – How The DAO Hack Changed Ethereum and Crypto.” https://www.coindesk.com/consensus-magazine/2023/05/09/coindesk-turns-10-how-the-dao-hack-changed-ethereum-and-crypto
[25] Ethereum Stack Exchange. (2017, November 7). “Explanation of Parity Library Suicide.” https://ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/30128/explanation-of-parity-library-suicide
[26] Medium – web3author. (2023, June 29). “PARITY Wallet Hack: What, When and How?” https://medium.com/@web3author/parity-wallet-hack-demystified-all-you-need-to-know-91b8dcb5b81
[27] Proskauer. (2017, December 22). “When Smart Contracts are Outsmarted: The Parity Wallet ‘Freeze’ and Software Liability in the Internet of Value.” https://www.proskauer.com/blog/when-smart-contracts-are-outsmarted-the-parity-wallet-freeze-and-software-liability-in-the-internet-of-value
[28] The Defiant. “Victims of $30M Parity Wallet Hack Offer Attacker $60M ‘Bounty’.” https://thedefiant.io/news/hacks/parity-wallet-hack-bug-bounty-stolen-eth
[29] GitHub – OpenEthereum. “anyone can kill your contract #6995.” https://github.com/openethereum/parity-ethereum/issues/6995
[30] TechCrunch. (2017, November 7). “A major vulnerability has frozen hundreds of millions of dollars of Ethereum.” https://techcrunch.com/2017/11/07/a-major-vulnerability-has-frozen-hundreds-of-millions-of-dollars-of-ethereum/
[31] David Gerard. (2017, November 8). “The latest Ethereum Parity wallet disaster, play by play.” https://davidgerard.co.uk/blockchain/2017/11/08/the-ethereum-parity-wallet-disaster-play-by-play/
[32] Coin Bureau. “Parity to Ethereum Foundation: One Hard Fork, Please.” https://coinbureau.com/smart-contracts/parity-ethereum-foundation-one-hard-fork-please/
[33] Reddit – Ethereum. (2017, June 2). “Statement on QuadrigaCX Ether contract error.” https://www.reddit.com/r/ethereum/comments/6ettq5/statement_on_quadrigacx_ether_contract_error/
[34] Bloomberg. (2019, February 4). “Crypto Exchange Founder Dies, Leaves Behind $200 Million Problem.” https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2019-02-04/crypto-exchange-founder-dies-leaves-behind-200-million-problem
[35] Vanity Fair. (2019, November 22). “The Secret Life and Strange Death of Quadriga Founder Gerald Cotten.” https://www.vanityfair.com/news/2019/11/the-strange-tale-of-quadriga-gerald-cotten
[36] OSC QuadrigaCX Report. “Where did the Funds go? A Detailed Breakdown.” https://www.osc.ca/quadrigacxreport/where-did-the-funds-go.html
[37] OSC QuadrigaCX Report. “Downfall of Quadriga (2018).” https://www.osc.ca/quadrigacxreport/downfall-of-quadriga.html
[38] Corporate Finance Institute. “What Was the Famous DAO Heist?” https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/cryptocurrency/dao-heist/
[39] Medium – web3author. (2023, June 19). “Unpacking the DAO Hack: Understanding the What, When, and Hows.” https://medium.com/@web3author/unpacking-the-dao-hack-understanding-the-what-when-and-hows-738b454eda76
[40] IEEE Spectrum. (2016, June 17). “DAO May Be Dead After $60 Million Theft.” https://spectrum.ieee.org/dao-may-be-dead-after-40million-theft
[41] Investopedia. (2025, April 14). “Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO).” https://www.investopedia.com/tech/what-dao/
[42] Digital Skills Jobs Europa. (2023, August 25). “The DAO Hack: Story of Ethereum Classic.” https://digital-skills-jobs.europa.eu/en/opportunities/learning-content/dao-hack-story-ethereum-classic
[43] ImmuneBytes. (2020, December 24). “A Detailed Analysis of what happens when Ether is Lost in a Transfer.” https://immunebytes.com/blog/a-detailed-analysis-of-what-happens-when-ether-is-lost-in-a-transfer/
[44] Ledger Academy. “A Guide to Ethereum Exploits and Security Best Practices.” https://www.ledger.com/ru/academy/topics/security/stronga-comprehensive-guide-to-ethereum-exploits-and-security-best-practicesstrong
[45] sFOX. (2018, September 14). “How to Secure Your Ether Wallet Against Theft in 10 Minutes.” https://www.sfox.com/blog/how-to-secure-your-ether-wallet-against-theft-in-10-minutes/
[46] Ethereum.org. (2024, September 13). “Ethereum security and scam prevention.” https://ethereum.org/en/security/
[47] MetaMask Support. “What is a ‘Secret Recovery Phrase’ and how to keep your crypto wallet secure.” https://support.metamask.io/start/learn/what-is-a-secret-recovery-phrase-and-how-to-keep-your-crypto-wallet-secure/
[48] Casa.io. “Ethereum Wallets.” https://casa.io/learn-more/ethereum-wallet
[49] QuickNode. (2025, March 18). “An Introduction to Crypto Wallets and How to Keep Them Secure.” https://www.quicknode.com/guides/web3-fundamentals-security/security/an-introduction-to-crypto-wallets-and-how-to-keep-them-secure
[50] Forbes. (2024, August 11). “A Guide To Ethereum Wallets: What They Are And How To Use One.” https://www.forbes.com/sites/digital-assets/article/ethereum-wallets-what-they-are-how-to-use-one/
[51] Coinbase. “How to keep your crypto secure.” https://www.coinbase.com/learn/crypto-basics/how-to-secure-crypto
[52] Stader Labs. “Ethereum Security: A Comprehensive Guide About Best Staking Practices.” https://www.staderlabs.com/blogs/staking-basics/ethereum-security/
[53] Hacken. (2023, March 21). “Wallet Security: Best Practices For Keeping Your Crypto Safe.” https://hacken.io/discover/wallet-security/
[54] Trust Wallet. (2025, February 7). “How to Safely store Bitcoin, Ethereum and other Cryptocurrencies.” https://trustwallet.com/blog/crypto-basics/how-to-safely-store-bitcoin-ethereum-and-other-cryptocurrencies
[55] Rapid Innovation. “Ultimate Crypto Wallet Security Guide 2024.” https://www.rapidinnovation.io/post/cryptocurrency-wallet-security-best-practices-and-tips
[56] MyEtherWallet. (2019, July 18). “The 5 Most Common User Issues in Crypto and How to Prevent Them.” https://www.myetherwallet.com/blog/common-crypto-user-issues/
[57] SimpleSwap. “Ethereum (ETH) Wallets: A Complete Guide.” https://simpleswap.io/blog/best-ethereum-wallets
[58] ZenLedger. “Secure Your ETH: Discover The Best Ethereum Wallets of 2024!” https://zenledger.io/blog/best-ethereum-wallets/
[59] Apriorit. (2024, December 10). “Crypto Wallet Security Best Practices.” https://www.apriorit.com/dev-blog/crypto-wallet-security-best-practices
[60] Remitano. (2025, June 22). “Crypto Wallet Security: Best Practices to Keep Coins Safe.” https://remitano.com/uy/forum/154583-crypto-wallet-security-best-practices-to-keep-coins-safe
[61] Exodus Support. “How do I keep my money safe? How to store cryptocurrency safely.” https://support.exodus.com/support/en/articles/8598632-how-do-i-keep-my-money-safe-how-to-store-cryptocurrency-safely
[62] Medium – CoinCapture. (2024, March 8). “A Comprehensive Guide To Setting Up And Managing An Ethereum Wallet.” https://medium.com/@coinscapture/a-comprehensive-guide-to-setting-up-and-managing-an-ethereum-wallet-1ff88631bf98
[63] Off The MRKT. (2024, September 23). “Ethereum Wallets Explained: How to Store Your ETH Safely.” https://www.offthemrkt.com/lifestyle/ethereum-wallets-explained-how-to-store-your-eth-safely
[64] Reddit – ethtrader. (2024, December 23). “Ultimate Guide To Secure Your Crypto Wallet.” https://www.reddit.com/r/ethtrader/comments/1hkjy4p/ultimate_guide_to_secure_your_crypto_wallet/
[65] Everstake. (2023, August 21). “What Validators Do to Prevent Slashing in Ethereum.” https://everstake.one/blog/what-validators-do-to-prevent-slashing-in-ethereum
[66] KeychainX. “Recover Ethereum Password guide.” https://keychainx.io/recover-ethereum-password/
[67] CryptoSlate. (2025, February 28). “Ethereum’s Vitalik Buterin calls for wallet security focus to prevent irreversible crypto losses.” https://cryptoslate.com/ethereums-vitalik-buterin-calls-for-wallet-security-focus-to-prevent-irreversible-crypto-losses/
[68] OpenZeppelin. “Smart Contract Security.” https://docs.openzeppelin.com/learn/
[69] Ethereum Magicians. (2018, April 15). “EIP-999: Restore Contract Code at 0x863DF6BFa4.” https://ethereum-magicians.org/t/eip-999-restore-contract-code-at-0x863df6bfa4/130
[70] DeFiSafety. “DeFi Protocol Safety Reviews.” https://defisafety.com/
[71] Candide. (2023, March 9). “Making Ethereum Accounts Recoverable – The Seedless Way.” https://docs.candide.dev/blog/making-accounts-recoverable/
[72] Dynamic.xyz. (2022, June 3). “Recovery Methods in Wallets – An Overview.” https://www.dynamic.xyz/blog/recovery-methods-in-wallets-an-overview
[73] ReWallet. “How to Recover Your Ethereum Presale Wallet.” https://rewallet.de/en/blog/ethereum-presale-wallet-recovery/
[74] CryptoRecovers. “Recover ETH Presale: Access Ethereum Presale Wallet in 2025.” https://cryptorecovers.com/blog/recover-ethereum-eth-presale/
[75] MyEtherWallet. (2021, January 27). “How to Recover Your Old Ethereum Wallet with MEW.” https://www.myetherwallet.com/blog/recover-your-old-ethereum-wallet-with-mew/
[76] Cointelegraph Learn. (2024, August 14). “How to recover a crypto wallet with or without a seed phrase.” https://cointelegraph.com/learn/articles/how-to-recover-a-crypto-wallet
[77] RapidAPI. “How To Recover Stolen Ethereum.” https://rapidapi.com/wizard-asset-recovery-wizard-asset-recovery-default/api/how-to-recover-stolen-ethereum
[78] CoinCashew. (2024, May 14). “Guide | Recover Ethereum Validator Mnemonic Seed.” https://www.coincashew.com/coins/overview-eth/guide-or-recover-ethereum-validator-mnemonic-seed
[79] Datarecovery.com. (2021, October 14). “How DAO Hack Victims Can Still Recover Ether.” https://datarecovery.com/2021/10/how-dao-hack-victims-can-still-recover-ether/
[80] Ethereum Improvement Proposals. “EIP-4337: Account Abstraction Using Alt Mempool.” https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-4337
[81] Medium – Alex Van de Sande. (2018, April 24). “Recovering lost ether, past and future.” https://avsa.medium.com/recovering-lost-ether-past-and-future-eeb38b17aeb5
[82] Codacy Blog. (2017, November 21). “Ethereum: Preventing a $170 million loss | Bug With Crypto Wallet.” https://blog.codacy.com/how-the-170-million-ethereum-bug-could-have-been-prevented
[83] GitHub – vittominacori. “eth-token-recover: TokenRecover allows to recover any ERC-20 or NFT.” https://github.com/vittominacori/eth-token-recover
[84] Coinbase Help. “Recover unsupported crypto.” https://help.coinbase.com/en/coinbase/trading-and-funding/sending-or-receiving-cryptocurrency/recover-unsupported-crypto
[85] Bitcoin.com Support. “Recovering your ETH wallet.” https://support.bitcoin.com/en/articles/5172126-recovering-your-eth-wallet
[86] Northeastern University – Abhi Shelat. “The 2nd Parity Multi-sig Wallet $300m Error.” https://shelat.khoury.northeastern.edu/17f-money/300m-parity-bug-part2/
[87] OpenZeppelin Blog. (2017, November 7). “The Parity Wallet Hack Reloaded.” https://blog.openzeppelin.com/parity-wallet-hack-reloaded
[88] Crowell & Moring. (2016, June 27). “The DAO Hack Provides Lessons for Companies Using Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology.” https://www.crowell.com/en/insights/client-alerts/the-dao-hack-provides-lessons-for-companies-using-blockchain-and-distributed-ledger-technology
[89] Ethereum Stack Exchange. (2016, August 20). “Lost ether: wallet on some other chain.” https://ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/8171/lost-ether-wallet-on-some-other-chain
[90] CoinMarketCap Academy. “A History of ‘The DAO’ Hack.” https://coinmarketcap.com/academy/article/a-history-of-the-dao-hack
[91] Frontiers in Blockchain. (2020, May 26). “The DAO Controversy: The Case for a New Species of Corporate Governance?” https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/blockchain/articles/10.3389/fbloc.2020.00025/full
[92] Bitstamp Learn. (2023, July 17). “Ethereum DAO Hack.” https://www.bitstamp.net/learn/crypto-101/ethereum-dao-hack/
[93] Liquidity Provider. (2024, February 13). “What Was The DAO? Story of Infamous Hack.” https://liquidity-provider.com/articles/what-was-the-dao-the-story-of-infamous-hack/
[94] Cybereason. “Malicious Life Podcast: The Ethereum DAO Hack.” https://www.cybereason.com/blog/malicious-life-podcast-the-ethereum-dao-hack
[95] SSRN. “The DAO Attack.” https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm/SSRN_ID3077683_code1882865.pdf
[96] Quora. (2024, September 26). “I just lost my Ethereum. How can I recover it back urgently?” https://www.quora.com/I-just-lost-my-Ethereum-How-can-I-recover-it-back-urgently
[97] Reddit – Ethereum. (2021, January 4). “Any good methods for recovering a lost wallet password?” https://www.reddit.com/r/ethereum/comments/kqiv1e/any_good_methods_for_recovering_a_lost_wallet/
[98] Blank Rome. (2019, February 5). “QuadrigaCX’s Insolvency: Problems in Tracing and Recovering Cryptocurrency When Keys Are Stored Offline.” https://www.blankrome.com/publications/quadrigacxs-insolvency-problems-tracing-and-recovering-cryptocurrency-when-keys-stored
[99] CoinDesk. (2022, December 19). “Bitcoin Addresses Tied to Defunct Canadian Crypto Exchange QuadrigaCX Wake Up.” https://www.coindesk.com/policy/2022/12/19/bitcoin-addresses-tied-to-defunct-canadian-crypto-exchange-quadrigacx-wake-up
[100] BBC. (2019, February 16). “Quadriga: The cryptocurrency exchange that lost $135m.” https://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-47203706
[101] Science Direct. “Dealing with blame in digital ecosystems: The DAO failure in the Ethereum blockchain.” https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040162525001271
[102] arXiv. (2021, January 15). “Security Analysis of DeFi: Vulnerabilities, Attacks and Advances.” https://arxiv.org/pdf/2101.06204
[103] YouTube – Films on VICE. (2025, March 24). “The Mysterious Death of Canada’s Crypto King.” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2VTjAguC-Fg
[104] YouTube – FD Finance. (2025, March 9). “The QuadrigaCX Fraud: The Ultimate Crypto Exit Scam?” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4jbXVzppF-s
[105] YouTube – Ethereum Breakdown. (2017, July 24). “The Parity Multisig Exploit ($32 million theft).” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VUH4gRDQYsA
[106] YouTube – ERC223 Tutorial. (2019, November 14). “Prevent tokens from being lost in smart contract.” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7yKvh8esaQw
[107] YouTube – FIX. (2020, August 15). “Stuck Transaction on Ethereum.” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J6xbcjNDFO0
[108] YouTube – Did Ethereum Sell Out. (2025, April 11). “The Controversial DAO Hack Explained.” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ae7ux_sM5OY
[109] CoinStats. “Shocking Revelation: Over 913K Ethereum Lost Permanently to Errors and Bugs.” https://coinstats.app/news/8313285fc9ec094bcc7ff81d3f5dc9c0aecd612c443d836216dc4fc2d962179f_Shocking-Revelation-Over-913K-Ethereum-Lost-Permanently-to-Errors-and-Bugs
[110] CoinLaw. (2025, July 20). “$3.4 Billion in Ether Lost Forever Due to Bugs and Mistakes.” https://coinlaw.io/ether-lost-3-4b-user-errors-bugs/
[111] Ainvest. (2025, July 21). “Ethereum News Today: Ether Lost to User Error and Bugs Surges 44% to 913,111 ETH.” https://www.ainvest.com/news/ethereum-news-today-ether-lost-user-error-bugs-surges-44-913-111-eth-2507/
[112] Etherscan. “Address 0x863df6bfa4469f3ead0be8f9f2aae51c91a907b4.” https://etherscan.io/address/0x863df6bfa4469f3ead0be8f9f2aae51c91a907b4
[113] Yahoo Finance. (2021, October 20). “Victims of $30M Parity Wallet Hack Offer Attacker $60M ‘Bounty’.” https://finance.yahoo.com/news/victims-30m-parity-wallet-hack-170550649.html
[114] Reddit – Ethereum. (2017, July 19). “Wallets created with Parity’s ‘Multisig’ feature have a critical vulnerability.” https://www.reddit.com/r/ethereum/comments/6oalcq/important_wallets_created_with_paritys_multisig/
[115] Reddit – Ethereum. (2018, January 7). “Lost all my ETH. Help my understand how.” https://www.reddit.com/r/ethereum/comments/7op7cx/lost_all_my_eth_help_my_understand_how/
[116] Reddit – Ethereum. (2023, June 23). “The DAO Hack that Changed Ethereum’s Destiny.” https://www.reddit.com/r/ethereum/comments/14h8tch/the_dao_hack_that_changed_ethereums_destiny/
[117] GitHub – Remix Project. (2025, January 15). “0.43 ETH has disappeared from my contract created on ethereum.” https://github.com/ethereum/remix-project/issues/5649
[118] HashNode – Noah Powell. (2024, August 1). “How to Recover Lost ETH or ERC20 Tokens.” https://trustedandlicensedcryptocurrencyrecoveryexpert.hashnode.dev/how-to-recover-lost-eth-or-erc20-tokens
[119] CryptoRecovers. (2025, April 10). “How to Recover Ether.li Wallet: Ethereum Recovery Guide.” https://cryptorecovers.com/blog/recover-ether-li-wallet-ethereum-recovery-guide/
[120] ReWallet. “Ether.li: A Comprehensive Guide to Ethereum Wallet Recovery.” https://rewallet.de/en/blog/ether-li-recovery/
[121] Medium – CoinCapture. (2024, March 8). “A Comprehensive Guide To Setting Up And Managing An Ethereum Wallet.” https://medium.com/@coinscapture/a-comprehensive-guide-to-setting-up-and-managing-an-ethereum-wallet-1ff88631bf98
[122] Ethereum.org. (2024). “The Merge.” https://ethereum.org/en/roadmap/merge/
[123] Ethereum.org. (2024). “Proof-of-stake.” https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/consensus-mechanisms/pos/
[124] Ethereum.org. (2024). “Staking.” https://ethereum.org/en/staking/
[125] Ethereum Foundation Blog. (2022). “The Merge is Complete.” https://blog.ethereum.org/2022/09/15/the-merge-is-complete